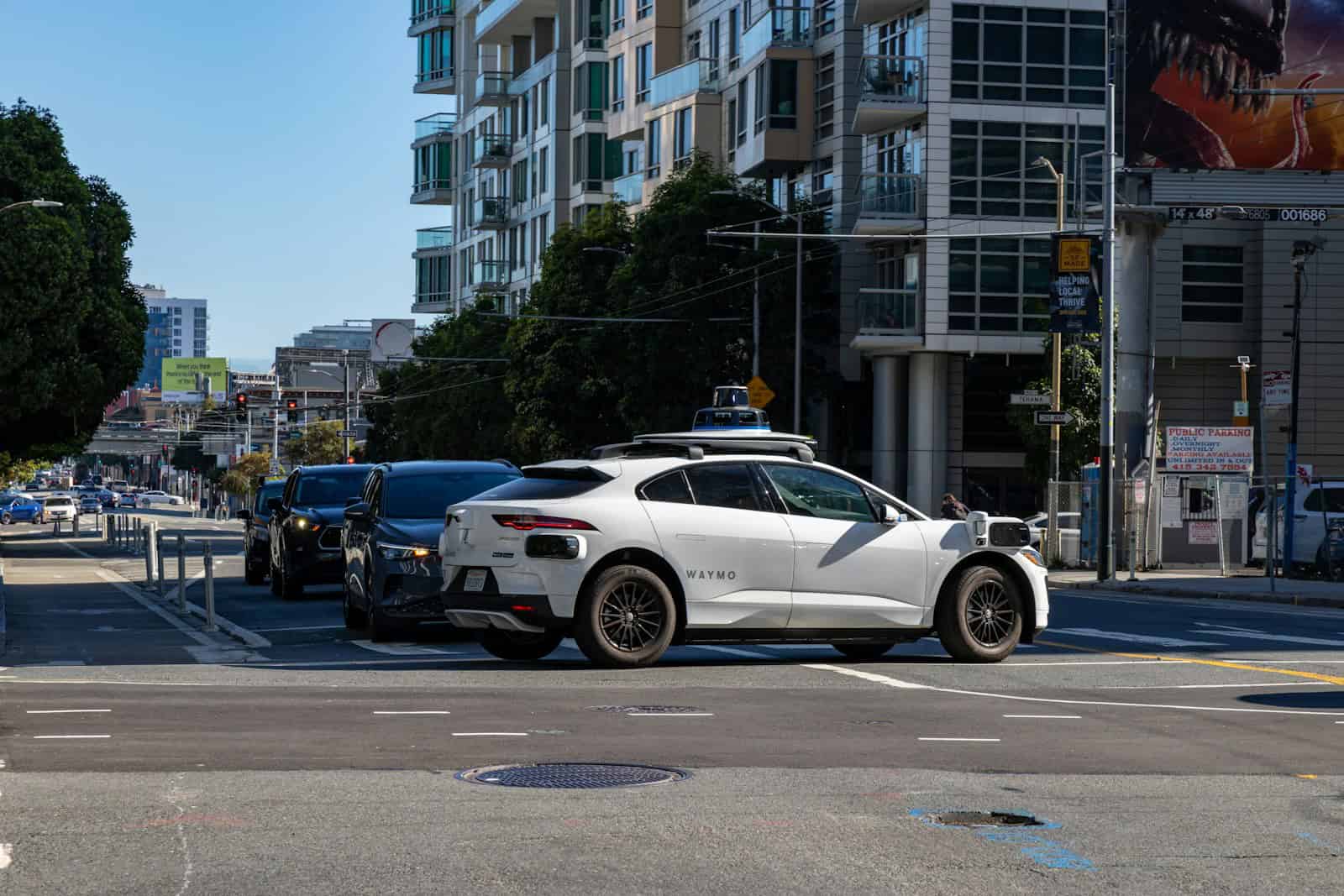
Waymo and Toyota have officially announced a strategic partnership that could reshape the future of autonomous driving—and directly challenge Tesla’s ambitions in the robotaxi space. The collaboration combines Waymo’s advanced self-driving software with Toyota’s world-renowned manufacturing capabilities to create a next-generation autonomous vehicle platform that will serve both commercial and personal-use markets.
Unlike previous partnerships that focused solely on ride-hailing fleets, this venture will explore deeper integration of Waymo’s Driver system into Toyota’s production vehicles, potentially giving consumers the option to own self-driving cars rather than just ride in them. Toyota’s dedicated autonomous division, Woven by Toyota, will play a central role in development, signaling how serious the automaker is about leapfrogging into the next era of mobility.
A Direct Response to Tesla’s Robotaxi Strategy

Tesla has long promised a future where millions of autonomous robotaxis operate without human drivers, powered entirely by its camera-based Full Self-Driving (FSD) system. CEO Elon Musk has even hinted that Tesla’s robotaxi debut is set for June 2025, starting in Austin, Texas. However, critics remain skeptical about the safety and scalability of a vision-only approach.
In contrast, Waymo’s system relies on a more robust sensor fusion approach, combining LiDAR, radar, and high-resolution cameras—a strategy many industry experts consider safer and more reliable in complex urban environments. By teaming up with Toyota, Waymo is not only extending its robotaxi service potential but also signaling readiness to scale production-grade autonomous vehicles in a way Tesla hasn’t yet achieved.
Shifting Industry Trends Toward Personally-Owned AVs
The partnership also reflects a broader shift in the industry. While robotaxi services like Waymo One (available in Phoenix and San Francisco) have been in public trials for years, consumer demand is increasingly leaning toward personally owned autonomous vehicles (POAVs). This shift has prompted legacy automakers like GM to pivot away from exclusive fleet-focused projects like Cruise and instead invest in scalable tech for individual car buyers.
Toyota and Waymo’s alliance positions them ahead of the curve. Instead of relying solely on fleet operations, they’re investing in hardware and software platforms that can eventually be offered in Toyota’s consumer vehicles—effectively democratizing access to full autonomy.
Why This Partnership Matters
- Waymo gains a global manufacturing powerhouse with proven scale and reliability.
- Toyota gets access to arguably the most mature AV software stack in the industry, avoiding the massive R&D overhead of building its own.
- The partnership brings realistic near-term potential for privately-owned self-driving vehicles, not just taxis.
- This strategic alignment strengthens both companies’ competitiveness against Tesla, Amazon-backed Zoox, and GM’s Cruise.
With pilot programs and production planning expected to ramp up later this year, the Toyota–Waymo alliance could represent a turning point for the mainstream adoption of autonomous vehicles. For consumers, it means one step closer to owning a car that can drive itself—and for Tesla, it means the competition is no longer just catching up, but possibly overtaking.
How Autonomous Driving Tech Stacks Up
As the race to dominate the self-driving vehicle market heats up, two major players—Waymo and Tesla—are heading in very different directions. Tesla, with its camera-only Full Self-Driving (FSD) system, is focused on scalability through consumer-owned electric vehicles. Waymo, owned by Alphabet (Google’s parent company), has taken a more conservative, sensor-rich approach with its Driver platform, which currently powers robotaxi services in several cities.
Now, with Waymo partnering with Toyota to expand its tech into both commercial fleets and personal vehicles, the question is clear: how do these two giants truly compare on the technology front?

Core Philosophy
| Feature | Waymo | Tesla |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy Approach | Full-stack autonomous software using LiDAR, radar, and cameras | Vision-only approach using 360-degree camera arrays |
| Target Use | Robotaxis and personally owned autonomous vehicles | Consumer EVs with Full Self-Driving software |
| Launch Strategy | Gradual rollout through geofenced zones, verified safety data | Bold nationwide rollout, even in unfinished beta form |
Sensor Suite & Hardware
| Feature | Waymo Driver | Tesla FSD |
|---|---|---|
| Cameras | 29 cameras around the vehicle | 8 exterior cameras |
| LiDAR | Yes – for 3D mapping, object detection, and safety redundancy | No – Tesla believes LiDAR is unnecessary |
| Radar | Yes – used for depth perception and adverse weather detection | Previously used; phased out as of 2021 |
| Compute Power | Custom onboard compute system from Alphabet with AI inference | Tesla-designed FSD chip, optimized for vision-based learning |
Software & Capabilities
| Feature | Waymo | Tesla |
|---|---|---|
| Mapping | Uses high-definition pre-mapped routes (HD maps) | Real-time processing with neural nets; no prior maps used |
| Environment Handling | Highly cautious and rule-bound in unfamiliar or complex zones | Dynamic decision-making, but occasionally aggressive or error-prone |
| Over-the-Air Updates | Yes – regularly improves driving behaviors | Yes – continuous software updates for FSD Beta |
| Driver Monitoring | N/A – no driver needed in robotaxis | Yes – interior cameras to monitor driver attention (required in FSD Beta) |
| Geofencing | Yes – only operates in verified zones (e.g., SF, Phoenix) | No – designed to operate anywhere, but with inconsistent results |
Real-World Deployment
| Feature | Waymo | Tesla |
|---|---|---|
| Robotaxi Services | Fully driverless in Phoenix and limited areas of San Francisco | Planned 2025 pilot launch in Austin, Texas |
| Accident Record Transparency | Publicly available crash data; strict safety reporting | Mixed transparency; FSD Beta accidents under public scrutiny |
| Driverless Approval | DMV-approved in California and Arizona | Still requires a licensed driver in the vehicle (U.S.) |
| User Experience | Hailed via app, no steering wheel in custom robotaxi units | FSD requires user input in tricky situations |
AI & Machine Learning
Waymo has spent over a decade refining its AI with millions of real-world and simulated miles. It operates conservatively, prioritizing predictability and safety over human-like assertiveness. Tesla, by contrast, relies heavily on AI-trained neural networks that interpret live camera feeds, attempting to mimic how humans drive using vision alone—sometimes at the expense of consistency.
Final Thoughts: Conservative Precision vs. Bold Innovation
Waymo represents the gold standard in safety, redundancy, and slow-but-sure deployment. Its partnership with Toyota could finally give it the production volume needed to bring self-driving tech to everyday car buyers.
Tesla, meanwhile, is pushing boundaries with an audacious, software-first approach. While its FSD Beta remains controversial, Tesla is betting big on a scalable, vision-only model that could revolutionize autonomous driving—if it works.
Each approach has its risks. Waymo may scale too slowly to outpace competitors. Tesla may reach consumers first but face bigger legal and safety hurdles. But now, with Toyota’s global reach behind Waymo, the gap may be closing faster than anyone expected.
Key Takeaways
- Waymo and Toyota are partnering to build a new autonomous vehicle platform combining their respective strengths.
- The collaboration aims to bring self-driving technology to personally-owned vehicles, expanding beyond robotaxi services.
- This partnership could speed up the wider adoption of autonomous driving technology in everyday consumer cars.
Details of the Waymo-Toyota Autonomous Vehicle Collaboration
The newly announced partnership between Waymo and Toyota marks a significant step forward in the autonomous vehicle industry, combining Toyota’s manufacturing expertise with Waymo’s self-driving technology to create a purpose-built platform for driverless transportation.
Overview of the Strategic Partnership
Waymo and Toyota have announced a strategic partnership focused on developing a new autonomous vehicle platform. This collaboration brings together two industry giants with complementary strengths.
Toyota brings decades of car manufacturing expertise and global scale to the table. Their production capabilities will be crucial for mass production of the new vehicles.
Waymo contributes its advanced self-driving technology called Waymo Driver, which has already logged millions of miles on public roads. The company’s experience operating robotaxi services gives it valuable real-world data.
The partnership aims to accelerate the adoption of autonomous vehicles by creating vehicles specifically designed for self-driving from the ground up, rather than retrofitting existing models.
Objectives and Goals of the New Autonomous Platform
The primary goal of this collaboration is to develop a purpose-built autonomous vehicle platform that integrates Waymo’s self-driving technology directly into Toyota’s vehicle architecture. This approach promises better performance than current retrofitted solutions.
The companies plan to focus on both passenger vehicles and commercial applications. They aim to create vehicles that can operate in various environments and weather conditions.
Safety stands as the top priority, with both companies committed to exceeding current safety standards for autonomous vehicles. The platform will incorporate multiple redundancy systems.
According to their joint statement, cost efficiency is another key objective. By designing vehicles specifically for autonomy, they hope to reduce the current high costs associated with self-driving technology.
The companies have not announced a specific timeline but indicated that development work has already begun.
Key Technologies and Innovations Involved
The partnership will leverage Waymo’s advanced autonomous driving system that includes:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- Camera arrays and radar systems
- Proprietary AI software for navigation and decision-making
- Cloud infrastructure for vehicle-to-vehicle communication
Toyota will contribute its expertise in:
- Vehicle platform design optimized for autonomous systems
- Battery and power management technology
- Manufacturing processes for scale production
- Vehicle safety systems and redundancy engineering
The collaboration may focus on building an electric vehicle platform, though this hasn’t been explicitly confirmed. Both companies recognize the advantages of electric powertrains for autonomous vehicles, including simplified mechanical systems.
Special attention will be given to developing a robust hardware architecture that can handle the massive computing power required for autonomous driving.
Role of Waymo and Toyota in the Development Process
Waymo will lead the development of the autonomous driving system, including sensors, computing hardware, and the AI software stack. Their team will handle the integration of these systems into the vehicle platform.
The company will also contribute its expertise in mapping, simulation testing, and real-world validation processes that have been refined through its Waymo One ride-hailing service.
Toyota will design and engineer the vehicle platform itself, ensuring it meets global safety standards and can be manufactured at scale. Their role includes creating the physical architecture that houses Waymo’s technology.
The Japanese automaker will also take the lead on production planning, supply chain management, and manufacturing infrastructure. This includes adapting existing factories to produce the new autonomous vehicles.
Both companies will share responsibility for testing and validation, with a joint team overseeing real-world trials before any commercial launch.
Impact and Implications of the Waymo-Toyota Partnership
The collaboration between Waymo and Google’s parent company Alphabet will reshape autonomous vehicle development and deployment across multiple sectors. This strategic alliance combines Toyota’s manufacturing expertise with Waymo’s leading self-driving technology.
Potential Effects on the Autonomous Vehicle Industry
This partnership is likely to accelerate autonomous vehicle development industry-wide. Waymo’s autonomous driving system combined with Toyota’s global manufacturing scale creates a powerful force in the market.
Competitors like Tesla, Mercedes-Benz, and Volvo may need to form similar alliances to keep pace. The partnership could standardize certain autonomous driving technologies, potentially creating new benchmarks for the industry.
Toyota gains access to Waymo’s advanced AI and sensor technology, while Waymo benefits from Toyota’s vehicle design expertise and production capabilities. This combination addresses a key industry challenge: scaling production of purpose-built autonomous vehicles.
The collaboration may trigger consolidation among smaller players who cannot match the resources of this partnership. Self-driving startups might seek acquisition or partnership with other major automakers.
How the Collaboration Will Influence Urban Transportation
Cities like Phoenix, San Francisco, and Austin where Waymo already operates could see faster expansion of robotaxi services. The partnership may help overcome current limitations in vehicle availability.
Urban planners will likely need to adapt infrastructure for a growing fleet of autonomous vehicles. Smart traffic systems, dedicated lanes, and specialized pickup zones might become more common in forward-thinking cities.
The partnership could accelerate the shift away from private car ownership in urban areas. More reliable and widely available autonomous services might convince city dwellers to use on-demand transportation instead of owning vehicles.
Transportation network companies like Uber and Lyft may face new competition as Waymo-Toyota vehicles enter the rideshare market. These companies might partner with other autonomous vehicle developers to remain competitive.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Safety improvements are a key focus of the Toyota-Waymo collaboration. Toyota’s reputation for reliability combined with Waymo’s safety record could set new standards for the industry.
Regulatory agencies will closely monitor this partnership’s developments. The collaboration’s scale may influence how governments approach autonomous vehicle legislation.
Key safety metrics to watch:
- Accident rates compared to human drivers
- System failure frequencies and severity
- Weather and road condition performance
- Cybersecurity protections
Privacy concerns will need addressing as more vehicles collect data about passengers and surroundings. The partnership must balance data collection needs with passenger privacy protections.
Comparison with Other Industry Partnerships
The Waymo-Toyota partnership differs from other collaborations in its comprehensive approach. While competitors focus on specific technologies, this alliance aims to develop a complete autonomous vehicle platform.
Major Industry Partnerships Comparison:
| Partnership | Focus Area | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waymo-Toyota | Full platform development | Manufacturing scale + AI expertise | Early development stage |
| Cruise-GM | Urban robotaxis | Strong US market presence | Limited global reach |
| Tesla (solo) | Consumer vehicles | Vertical integration | Limited partnerships |
| Mobileye-BMW | ADAS systems | Safety focus | Not fully autonomous |
Unlike Tesla’s primarily solo approach, the Waymo-Toyota partnership leverages complementary strengths. Tesla must build everything in-house, while this collaboration combines two industry leaders’ expertise.
The partnership may advance faster than others due to combining respective strengths in autonomous technology and vehicle manufacturing. This could lead to faster commercial deployment than competitors still developing core technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Waymo-Toyota partnership aims to advance autonomous driving technology through collaborative development. The companies have agreed to explore this joint venture to create a new self-driving platform for future vehicles.
What are the objectives of the partnership between Waymo and Toyota?
The main goal of this partnership is to speed up the development of autonomous driving technology. Waymo and Toyota plan to jointly create an autonomous driving system for future vehicle models.
This collaboration also focuses on expanding beyond Waymo’s current ride-hailing service. Waymo has been working on its Waymo One service but is now looking beyond that approach by partnering with Toyota.
How will Waymo’s technology be integrated into Toyota’s vehicles?
The partnership suggests that Waymo’s self-driving technology may be integrated into Toyota cars that consumers can buy. This marks a shift from Waymo’s previous focus on ride-hailing services to consumer vehicles.
The companies are exploring ways to combine Waymo’s autonomous driving expertise with Toyota’s vehicle manufacturing skills. The goal is to create cars with advanced self-driving features that are safe and reliable for everyday use.
What potential impacts could the Waymo-Toyota collaboration have on the autonomous vehicle industry?
This partnership could speed up the wider adoption of self-driving technology in the consumer market. When two major players join forces, it often leads to faster innovation.
The collaboration might push other companies to form similar partnerships. This could create healthy competition that benefits consumers through better and safer autonomous vehicles.
What advancements in autonomous driving technology can be expected from the Waymo-Toyota partnership?
The partnership will likely focus on improving current self-driving systems. Waymo’s autonomous driving technology, formerly the Google self-driving car project, combined with Toyota’s manufacturing expertise could lead to more reliable systems.
We might see advancements in safety features, navigation capabilities, and user interfaces. The goal would be to create autonomous systems that work well in various driving conditions and environments.
How does the partnership between Waymo and Toyota differ from other alliances in the autonomous vehicle sector?
This partnership brings together Waymo’s software expertise with Toyota’s manufacturing prowess. Unlike some partnerships that focus only on testing or limited deployment, this one aims to develop technology for consumer vehicles.
The collaboration plans to create autonomous systems that could be built into cars consumers would buy, not just for ride-sharing fleets. This consumer focus sets it apart from many other autonomous driving partnerships.
What timeline has been projected for the development and deployment of the new autonomous vehicle platform?
The companies have not announced a specific timeline for the development or release of their joint autonomous platform. They have only stated that they have agreed to explore collaboration at this stage.
The development of autonomous vehicles typically takes several years from initial partnership to market-ready products. The companies will likely provide more details about their timeline as the project progresses.