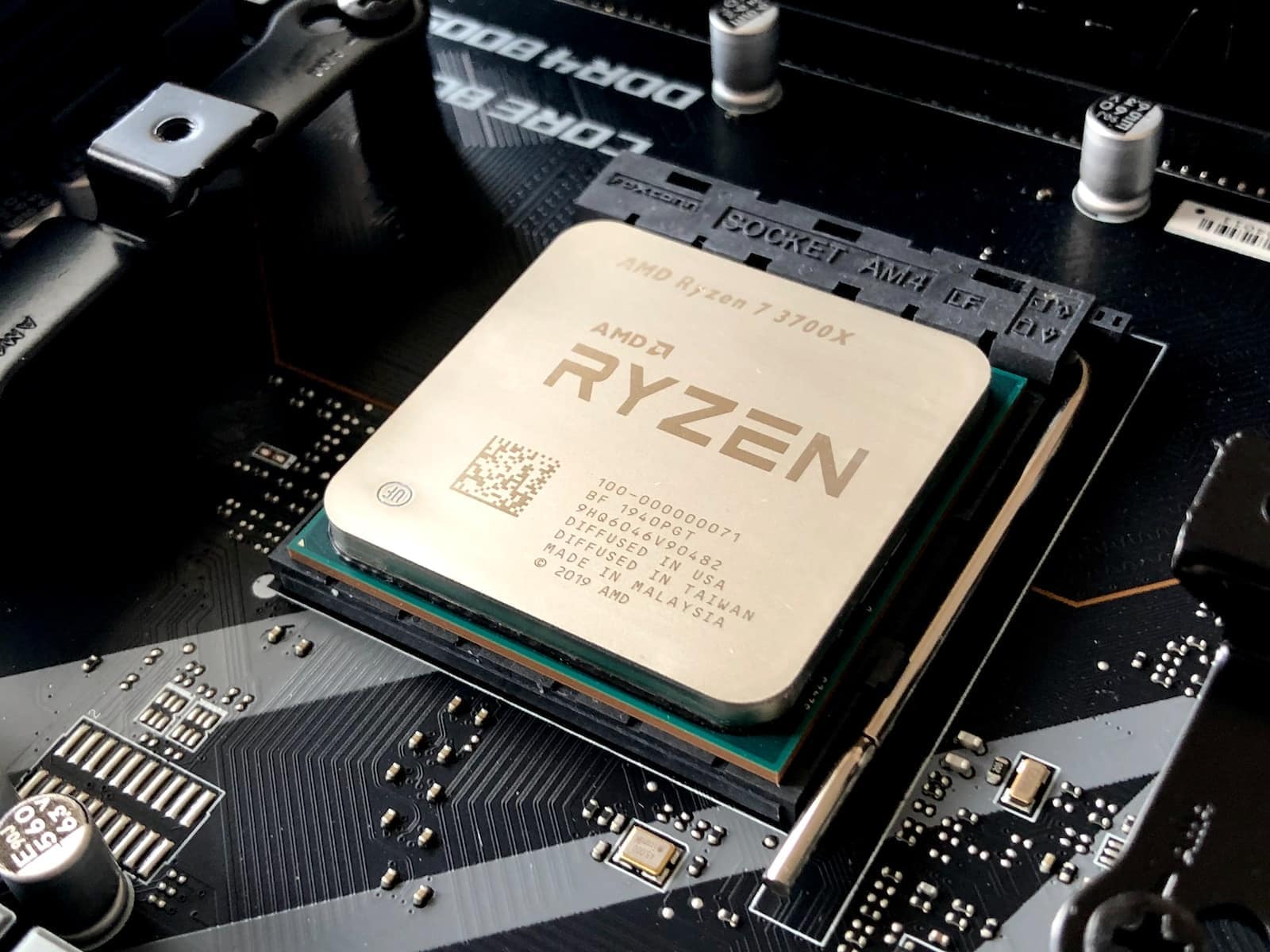
AMD’s Ryzen processors have become a popular choice for gamers, content creators, and everyday computer users. This is due to their impressive performance and competitive price points. If you’re building or upgrading a PC, understanding the different options within the AM4 socket is essential.
What To Know About AM4 Socket CPUs
What is an AM4 socket?
The AM4 socket is a physical connection point on your motherboard designed to accommodate a specific type of processor. AMD has used the AM4 socket for several generations of Ryzen processors, offering excellent compatibility and upgrade paths.
Popular AM4 Processors
Here’s a table outlining some popular AM4 socket CPUs from AMD’s Ryzen lineup:
| Processor Model | Cores/Threads | Base Clock (GHz) | Max Boost (GHz) | TDP (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 5 1400 | 4/8 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 65 |
| Ryzen 5 4500 | 6/12 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 65 |
| Ryzen 5 5500 | 6/12 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 65 |
| Ryzen 7 1700 | 8/16 | 3.0 | 3.7 | 65 |
| Ryzen 7 5800X | 8/16 | 3.8 | 4.7 | 105 |
Things to consider when choosing:
- Number of cores and threads: More cores and threads enable better multitasking and handling demanding workloads.
- Clock speed: Higher clock speeds translate to faster single-core performance, important for tasks like gaming.
- TDP (Thermal Design Power): A higher TDP generally indicates more powerful processors but also higher power consumption and heat generation.
Benefits of AM4 CPUs
- Excellent compatibility: AM4 CPUs support a wide range of motherboards across different generations.
- Upgrade paths: You can easily upgrade your AM4 CPU to a newer, more powerful model without changing your motherboard.
- Value for money: AM4 CPUs offer competitive performance at attractive prices compared to their Intel counterparts.
Complete List
| CPU | Cores | Clock | TDP | Graphics |
| AMD A10-9700 | 4 | 3.5 GHz | 65 W | Radeon R7 (on-die) |
| AMD A10-9700E | 4 | 3 GHz | 35 W | Radeon R7 (on-die) |
| AMD A12-9800 | 4 | 3.8 GHz | 65 W | Radeon R7 (on-die) |
| AMD A12-9800E | 4 | 3.1 GHz | 35 W | Radeon R7 (on-die) |
| AMD A6-9500 | 2 | 3.5 GHz | 65 W | Radeon R5 (on die) |
| AMD A6-9500E | 2 | 3 GHz | 35 W | Radeon R5 (on die) |
| AMD A6-9550 | 2 | 3.8 GHz | 65 W | Radeon R5 (on die) |
| AMD A8-9600 | 4 | 3.1 GHz | 65 W | Radeon R7 (on-die) |
| AMD Athlon 200GE | 2 | 3.2 GHz | 35 W | Radeon Vega 3 |
| AMD Athlon 220GE | 2 | 3.4 GHz | 35 W | Radeon Vega 3 |
| AMD Athlon 240GE | 2 | 3.5 GHz | 35 W | Radeon Vega 3 |
| AMD Athlon 3000G (14nm) | 2 | 3.5 GHz | 35 W | Radeon Vega 3 |
| AMD Athlon X4 940 | 4 | 3.2 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Athlon X4 950 | 4 | 3.5 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Athlon X4 970 | 4 | 3.8 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 3 1200 (12nm) | 4 | 3.1 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 3 1200 (14nm) | 4 | 3.1 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 3 1300X | 4 | 3.5 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 3 2200G | 4 | 3.5 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3100 | 4 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3200G | 4 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 3 3300X | 4 | 3.8 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 3 4100 | 4 | 3.8 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 1400 | 4 | 3.2 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 1500X | 4 | 3.5 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 1600 (12nm) | 6 | 3.2 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 1600 (14nm) | 6 | 3.2 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 1600X | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 95 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 2400G | 4 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 11 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 2600 | 6 | 3.4 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 2600X | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 95 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3400G | 4 | 3.7 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 11 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3500 | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3500X | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600 | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600X | 6 | 3.8 GHz | 95 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 3600XT | 6 | 3.8 GHz | 95 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 4500 | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 4600G | 6 | 3.7 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 7 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5500 | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5500GT | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 7 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600 | 6 | 3.5 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600G | 6 | 3.9 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 7 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600GT | 6 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 7 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600X | 6 | 3.7 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 5 5600X3D | 6 | 3.3 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 1700 | 8 | 3 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 1700X | 8 | 3.4 GHz | 95 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 1800X | 8 | 3.6 GHz | 95 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 2700 | 8 | 3.2 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 2700X | 8 | 3.7 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3700X | 8 | 3.6 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3800X | 8 | 3.9 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 3800XT | 8 | 3.9 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5700 | 8 | 3.7 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5700G | 8 | 3.8 GHz | 65 W | Radeon Vega 8 |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5700X | 8 | 3.4 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5700X3D | 8 | 3 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800X | 8 | 3.8 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D | 8 | 3.4 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 9 3900 | 12 | 3.1 GHz | 65 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 9 3900X | 12 | 3.8 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 9 3900XT | 12 | 3.8 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 9 3950X | 16 | 3.5 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5900X | 12 | 3.7 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5900XT | 16 | 3.3 GHz | 105 W | None |
| AMD Ryzen 9 5950X | 16 | 3.4 GHz | 105 W | None |
Overview of AMD Ryzen AM4 CPUs
AMD’s Ryzen processors for the AM4 socket have revolutionized the CPU market with their impressive performance and power efficiency. They’re compatible with DDR4 memory and PCIe 4.0, offering a significant bandwidth for graphics and NVMe storage.
Evolution of the Ryzen Series
The Ryzen series, from the original 1000 models to the latest 5000 series, showcases AMD’s commitment to innovation. Starting with the first-generation Zen architecture, the Ryzen processors have seen consistent enhancements. With each new release, such as the Zen 2 and Zen 3, AMD has provided consumers with increased speed, more efficient power usage, and better overall performance. The introduction of Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) allowed for even more efficient handling of tasks.
- Ryzen 1000 Series (Zen): The start of a new era in AMD CPUs, offering solid performance.
- Ryzen 2000 Series (Zen+): Improved speed and efficiency over its predecessors.
- Ryzen 3000 Series (Zen 2): Brought significant enhancements, including support for PCIe 4.0.
- Ryzen 4000 Series (Zen 3): Focused on providing higher max boost speeds and increased cache size.
- Ryzen 5000 Series (Zen 4): The latest at this time, with even greater speed and efficiency.
While the Ryzen series includes a range of options like the affordable Athlon models, it also spans to the more powerful Ryzen 9 CPUs, catering to different needs and budgets.
Socket AM4 Platform Details
The Socket AM4 platform has become AMD’s standard for mainstream desktop CPUs. It supports AMD Ryzen processors and provides a versatile foundation for a variety of computer builds.
- Motherboard Compatibility: Most AM4 motherboards support multiple Ryzen generations, but it’s essential to check for BIOS updates.
- Memory and PCIe: DDR4 memory compatibility and PCIe 4.0 bandwidth are key features, enabling fast data transfer and storage speeds.
- Connectivity: Processor-direct SATA and USB connectivity are some of the notable aspects, adding to the appeal for gamers and creators who require quick data transfer rates.
The AM4 socket comfortably fits into the ecosystem of AMD chipsets, which have been designed to maximize the capabilities of Ryzen CPUs. As chipsets evolve to support newer technologies, users of the AM4 platform can look forward to updated features and sustained performance.
Ryzen AM4 CPU Models and Specifications
AMD’s Ryzen processors cover a broad spectrum of performance levels tailored for different users. From budget-friendly options to powerhouse chips, each category brings something unique to the table for computing on the AM4 platform.
Entry-Level Ryzen 3 Processors
Ryzen 3 represents AMD’s introductory lineup. Models like the Ryzen 3 1300X set a solid foundation with four cores, delivering reliable performance for everyday tasks and light gaming. Users find a good balance between cost and capability.
Mainstream Ryzen 5 Processors
The Ryzen 5 series offers mid-range performance, perfect for general users and gamers. For instance, the Ryzen 5 1600X and 2600 both come with six cores and 12 threads, striking a balance between price and performance. Later models, such as the Ryzen 5 5600 and 5600X, enhance this with even faster speeds and the newer 5600X3D, which introduces 3D V-Cache technology for a gaming edge.
High-Performance Ryzen 7 Processors
Moving up, Ryzen 7 caters to demanding users and gamers. Take the Ryzen 7 2700 and the Ryzen 7 1800X as examples, both offering eight cores and 16 threads for heavy multitasking and high-performance gaming. The Ryzen 7 5800 and 5800X further push these boundaries with improved architecture and clock speeds.
Enthusiast Ryzen 9 Processors
Ryzen 9 is at the top tier, targeting enthusiasts and professionals who crave the best. Processors like the AMD Ryzen 9 5900 and 5900X stand out with their 12 cores and 24 threads, providing top-of-the-line capabilities for intensive applications and ultimate gaming setups. They are the cream of the crop on the AM4 platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
When exploring AMD’s Ryzen AM4 CPUs, several common questions emerge. This section aims to address these queries with clear, accurate information.
What is the range of processors available in the AMD Ryzen AM4 lineup?
AMD’s AM4 platform hosts a variety of processors that cater to different market segments. These range from entry-level options such as the Ryzen 3 series to high-end models like the Ryzen 9 chips.
How does the performance of the Ryzen 7 compare to other AM4 CPUs?
The Ryzen 7 CPUs sit comfortably in the mid-to-high performance bracket within the AM4 family, delivering robust capabilities for gaming and productivity that outpace the Ryzen 5 yet fall slightly behind the top-tier Ryzen 9 in multitasking and high-demand scenarios.
Can I understand the performance hierarchy within the AMD Ryzen AM4 processors?
Yes, the hierarchy is straightforward: Ryzen 3 for budget builds, Ryzen 5 for mainstream users, Ryzen 7 for enthusiasts, and Ryzen 9 for the peak performance that enthusiasts and professionals seek.
What are the flagship models in the AM4 socket from the AMD Ryzen series?
The Ryzen 9 series, with CPUs like the Ryzen 9 5900X, represents the flagship offerings in the AM4 socket, delivering high core and thread counts for demanding applications.
Will AM4 motherboards support future AMD CPU releases?
While AM4 motherboards have supported multiple Ryzen generations, future compatibility depends on the technological advances and chipset support from AMD. As of now, any update on the next-gen CPU support would require an official statement from AMD.
How do different generations of AMD Ryzen CPUs compare in terms of performance?
With each new release, AMD’s Ryzen CPUs have shown performance gains, primarily due to improved architecture, increased core counts, and higher clock speeds, offering users enhanced computing experiences with each generation.