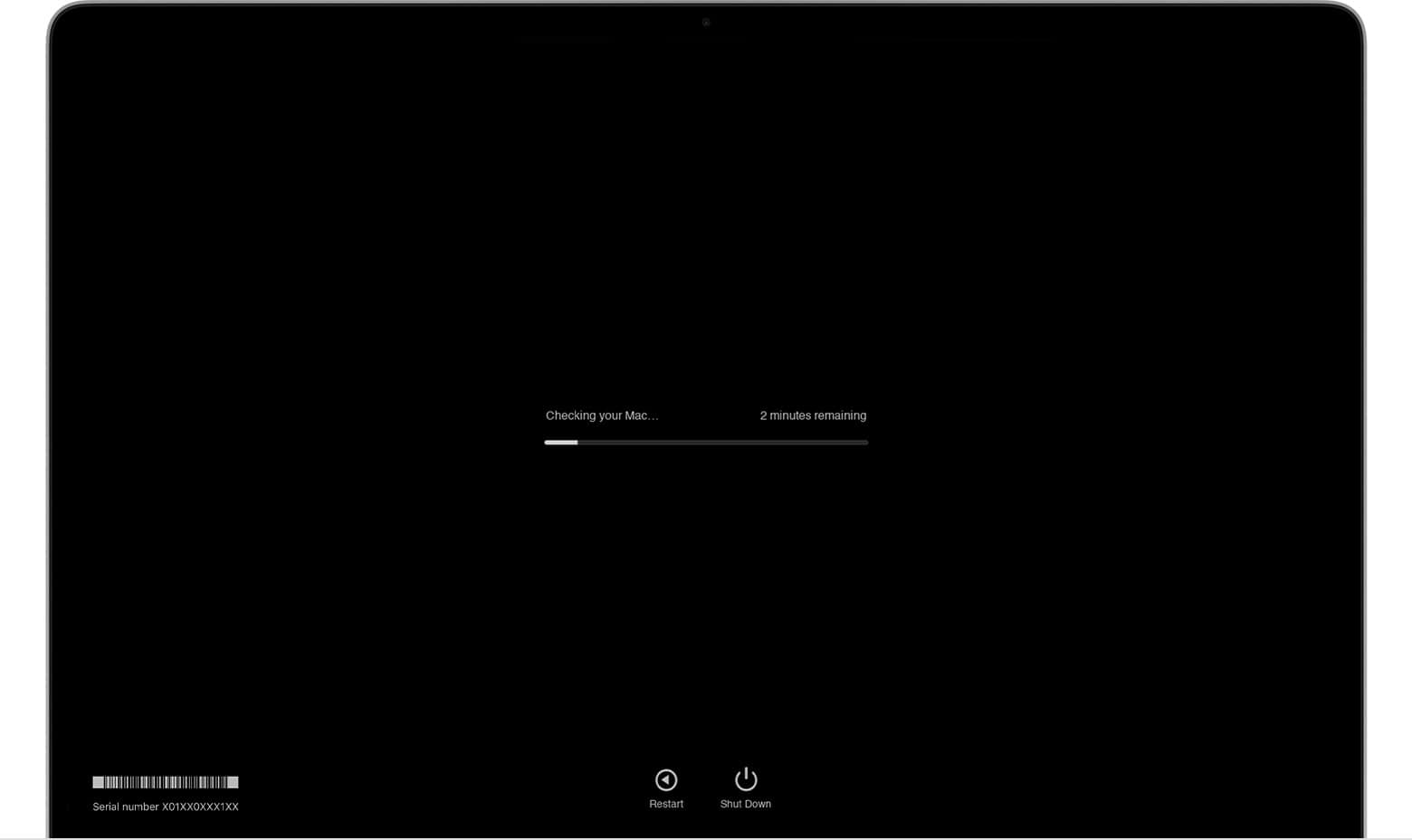
Keeping your Mac running smoothly is crucial for optimal performance. Apple provides a built-in tool called Apple Diagnostics to help you identify and troubleshoot hardware issues. You can run Apple Diagnostics on your Mac by restarting your computer and holding down the D key during startup.
This simple process allows you to check various hardware components. It tests your Mac’s logic board, memory, and wireless modules. The diagnostic tool then presents you with reference codes that point to specific problems if any are found.
Different Mac models may require slightly different steps to start the diagnostic process. For Apple silicon Macs, you’ll need to press and hold the power button while booting up, then press Command-D. Intel-based Macs made after June 2013 use the D key method mentioned earlier. Older Macs rely on the Apple Hardware Test instead.
| Mac Type | Diagnostic Method |
|---|---|
| Apple Silicon | Hold power button, press Command-D |
| Intel (post-June 2013) | Hold D key during startup |
| Intel (pre-June 2013) | Use Apple Hardware Test |
Keeping Your Mac Healthy: A Guide to Diagnostics Tests
Running diagnostics tests on your Mac can help you identify and fix problems. These tests check your Mac’s hardware and software for issues. Here’s how to run them:
Using Apple Diagnostics
Apple Diagnostics is a built-in tool that can help you find hardware problems. Here’s how to use it:
- Disconnect external devices: Remove any external devices connected to your Mac, except for the keyboard, mouse, display, and Ethernet connection.
- Turn off your Mac: Make sure your Mac is completely shut down.
- Turn on your Mac and press the “D” key: Press and hold the “D” key immediately after turning on your Mac. Keep holding it until you see the Apple Diagnostics screen.
- Choose your language: Select your preferred language.
- Run the test: Apple Diagnostics will automatically start running tests. This process may take a few minutes.
- Review the results: If any issues are found, you’ll see a reference code. You can use this code to get more information about the problem.
Using Apple Hardware Test
Older Macs may use Apple Hardware Test instead of Apple Diagnostics. The process is similar:
- Disconnect external devices: Remove any external devices connected to your Mac, except for the keyboard, mouse, display, and Ethernet connection.
- Turn off your Mac: Make sure your Mac is completely shut down.
- Insert the OS X Install Disc: If you have an older Mac, you may need to use the OS X Install Disc that came with your computer.
- Turn on your Mac and press the “D” key: Press and hold the “D” key immediately after turning on your Mac. Keep holding it until you see the Apple Hardware Test screen.
- Choose your language: Select your preferred language.
- Run the test: Apple Hardware Test will automatically start running tests. This process may take a few minutes.
- Review the results: If any issues are found, you’ll see an error code. You can use this code to get more information about the problem.
Other Diagnostic Tools
In addition to Apple Diagnostics and Apple Hardware Test, there are other diagnostic tools available for your Mac. These tools can provide more detailed information about your Mac’s hardware and software. Some popular options include:
- DriveDx: This tool can help you diagnose hard drive problems.
- MemTest86: This tool can help you test your Mac’s memory.
- Blackmagic Disk Speed Test: This tool can help you test the speed of your Mac’s storage devices.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
If you’re experiencing problems with your Mac, there are a few things you can try to fix them yourself:
- Restart your Mac: This can often resolve simple software glitches.
- Run Software Update: Make sure your Mac’s operating system is up to date.
- Check your internet connection: A slow or unstable internet connection can cause various problems.
- Free up storage space: If your Mac’s hard drive is full, it can slow down performance.
- Reset your Mac’s NVRAM or PRAM: This can sometimes resolve issues with your Mac’s settings.
If you’re still having problems after trying these steps, you may need to take your Mac to an Apple Store or an authorized service provider for further diagnosis and repair.
Maintaining Your Mac
Regular maintenance can help prevent problems and keep your Mac running smoothly. Here are a few tips:
- Keep your Mac clean: Dust and dirt can build up inside your Mac and cause overheating.
- Back up your data regularly: This will help you recover your data if your Mac crashes or is damaged.
- Use antivirus software: This can help protect your Mac from malware.
- Update your software regularly: Software updates often include bug fixes and security improvements.
- Monitor your Mac’s performance: Use Activity Monitor to track your Mac’s CPU, memory, and disk usage.
Preparing to Run Apple Diagnostics
Before running Apple Diagnostics, you need to take a few important steps. These steps ensure accurate results and smooth operation of the diagnostic tool.
Ensure Proper Shutdown and Power Supply
Shut down your Mac completely. Don’t use sleep mode or restart. A full shutdown clears temporary files and resets system processes.
Connect your Mac to a power outlet using the AC adapter. This prevents battery issues from interfering with the test.
Place your Mac on a flat, stable surface. Good ventilation helps prevent overheating during the diagnostic process.
Disconnecting External Devices
Unplug all external devices from your Mac. This includes:
- USB drives
- External hard drives
- Printers
- Monitors
- Ethernet cables
Leave only the power adapter, keyboard, and mouse connected. This isolates potential hardware issues to your Mac’s internal components.
Check for Active Network Connections
Turn off Wi-Fi on your Mac. Go to the Wi-Fi menu and select “Turn Wi-Fi Off”.
Disconnect any Ethernet cables. This ensures your Mac isn’t using an internet connection during diagnostics.
If you need to use Internet-based diagnostics, make sure you have a stable Wi-Fi connection available.
| Connection Type | Action |
|---|---|
| Wi-Fi | Turn off |
| Ethernet | Unplug cable |
| Bluetooth | Disable |
These steps help isolate your Mac’s hardware for accurate testing. They prevent external factors from affecting the diagnostic results.
Initiating Apple Diagnostics
Apple Diagnostics helps you test your Mac’s hardware for issues. The process differs slightly between Intel-based and Apple Silicon Macs.
Starting Diagnostics on Intel-Based Macs
To run Apple Diagnostics on an Intel Mac:
- Shut down your Mac
- Press the power button
- Immediately press and hold the D key
Release the D key when you see the progress bar or language selection screen. If this doesn’t work, try Option-D instead. This uses the internet version of Apple Diagnostics.
For Macs made before June 2013, you’ll use Apple Hardware Test. The steps are similar, but press and hold Option-D at startup.
| Mac Type | Key Combination |
|---|---|
| Intel (After June 2013) | D or Option-D |
| Intel (Before June 2013) | Option-D |
After the test runs, you’ll see results with reference codes. Write these down if you need to contact Apple Support.
Initiating Diagnostics on Apple Silicon Macs
For Macs with Apple Silicon chips:
- Press and hold the power button
- Keep holding until you see startup options
- Click Options > Continue
- Select a language if prompted
- Press Command-D
If your Mac has Touch ID, you can use it to select Options. The diagnostics will start automatically.
You might need to enter your admin password. The test takes 2-5 minutes. When finished, you’ll see results and any detected issues.
To rerun the test, click “Run the test again” or press Command-R. You can restart your Mac by clicking Restart or pressing R.
Understanding Diagnostic Reference Codes
Diagnostic reference codes provide crucial information about hardware issues on your Mac. These codes help pinpoint specific problems and guide troubleshooting efforts.
Interpreting Error Codes and Messages
When you run Apple Diagnostics on your Mac, you may encounter various error codes and messages. Each code corresponds to a specific hardware component or issue. For example, ADP000 indicates no problems were found, while CNW001 suggests a Wi-Fi hardware issue.
To interpret these codes:
- Note down the exact code displayed
- Visit Apple’s support website
- Look up the code in their reference guide
Some common codes include:
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| VFD002 | GPU issue |
| NDC001 | Wi-Fi hardware problem |
| PPT004 | Power adapter fault |
Understanding these codes helps you decide whether to attempt a fix yourself or seek professional help.
Apple Hardware Test and Apple Diagnostics Codes
Apple Hardware Test (AHT) and Apple Diagnostics are two tools used to check your Mac’s hardware. AHT was used in older Macs, while Apple Diagnostics is found in newer models.
Both tools generate similar reference codes, but their formats differ slightly:
- AHT codes: 3-digit or 4-digit numbers (e.g., 4ETH, 4IRP)
- Apple Diagnostics codes: Prefixed with letters (e.g., PPT001, NDC004)
To use these tools:
- Restart your Mac
- Hold the D key during startup
- Follow on-screen instructions
The test results will display any detected issues along with their corresponding codes. Keep these codes handy when contacting Apple Support or visiting an authorized service provider.
Post-Diagnostic Actions
After running diagnostics on your Mac, you may need to take further steps depending on the results. These actions can help resolve hardware issues, get professional assistance, or conduct more in-depth testing.
Exploring Solutions for Hardware Problems
If Apple Diagnostics identifies hardware issues, you can try several solutions. For memory problems, reseat or replace RAM modules. Clean dusty components with compressed air. Update your Mac’s firmware and drivers.
For persistent issues, consider these steps:
- Reset NVRAM/PRAM
- Perform an SMC reset
- Boot in Safe Mode to isolate software conflicts
Check cables and connections. Swap out external devices to rule out accessories as the cause. If possible, test components in another Mac to pinpoint faulty hardware.
Contacting Apple Support and Service Providers
When self-help fails, reach out to Apple Support. They can guide you through advanced troubleshooting steps. For in-person help, visit an Apple Store or contact an Authorized Service Provider.
Apple Support options:
- Phone support
- Online chat
- Support app
- Genius Bar appointments
Keep your Mac’s serial number handy. Describe the diagnostic results and steps you’ve taken. If under warranty, repairs may be free. AppleCare+ extends coverage and includes accidental damage protection.
Performing Extended Testing and Troubleshooting
For intermittent issues, run longer diagnostic tests. Use Activity Monitor to track resource usage and identify problematic processes. Check system logs for error messages.
Extended testing tools:
- Memtest for RAM
- Disk Utility’s First Aid
- Apple Hardware Test (for older Macs)
| Test Type | Duration | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Quick | 2-5 min | General check |
| Extended | 1-2 hours | Intermittent issues |
| Overnight | 8+ hours | Hard-to-replicate problems |
Use third-party diagnostic tools for deeper analysis. Boot from an external drive to isolate OS issues. Create a test user account to rule out user profile problems. Document all steps and results for future reference or support interactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Apple Diagnostics is a built-in tool for Mac users to check their hardware for issues. It’s easy to use and can help identify problems with your Mac’s components.
How to initiate Apple Diagnostics to troubleshoot my MacBook’s issues?
To start Apple Diagnostics on an Intel-based Mac, turn off your device and press the power button. Immediately hold the D key until you see a progress bar. For Apple Silicon Macs, press and hold the power button at startup, then press Command + D.
What are the steps to perform a system health check on a Mac computer?
First, shut down your Mac. Then restart it while holding the D key. Select your language when prompted. The diagnostic test will run automatically. After a few minutes, you’ll see the results on your screen.
How can I access system diagnostics on a Mac to check for problems?
You can access Apple Diagnostics even if your Mac won’t start normally. Restart your Mac and hold the D key during startup. This works for both Intel and Apple Silicon Macs. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the tests.
Is there an available diagnostic tool for Mac, and how do I use it?
Yes, Apple Diagnostics is available on all Macs. To use it, restart your Mac and hold the D key during startup. For Apple Silicon Macs, press and hold the power button, then press Command + D. The tool will check your Mac’s hardware and display any issues it finds.
Instructions for running a MacBook Air’s diagnostic tests?
To run diagnostics on a MacBook Air:
- Shut down your MacBook Air
- Press the power button to turn it on
- Immediately press and hold the D key
- Release the D key when you see a progress bar
- Choose your language if prompted
- Wait for the tests to complete
What should I do if Apple Diagnostics fails to start or work properly?
If Apple Diagnostics won’t start, try these steps:
- Disconnect all external devices except the keyboard and mouse
- Ensure your Mac is on a flat, stable surface with good ventilation
- Try using Apple Diagnostics over the internet by holding Option-D at startup
- If issues persist, contact Apple Support for further assistance
| Issue | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Won’t start | Disconnect external devices |
| No internet | Use built-in diagnostics (D key) |
| Freezes during test | Restart and try again |
| Error codes | Note them and contact Apple Support |