Many iPhone users worry about Trojan viruses infecting their devices, but the reality is more nuanced than most think. While iPhones are generally more secure than Android devices thanks to Apple’s strict App Store review process and sandboxed operating system, they aren’t completely immune to malware threats. Trojans on iPhones are rare but possible, particularly on jailbroken devices that bypass Apple’s built-in security measures.
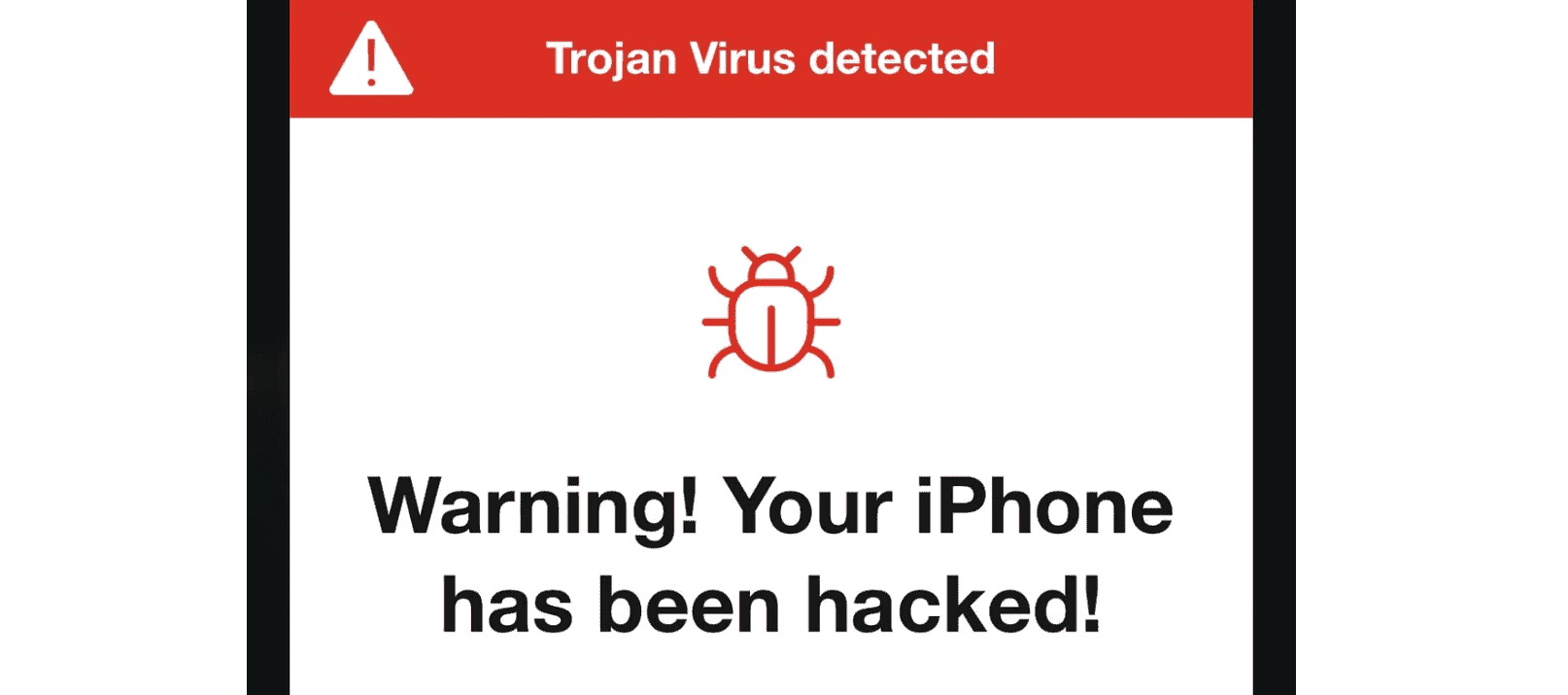
People often mistake legitimate pop-ups or website notifications for malware. These false warnings might claim your iPhone is infected and prompt you to download “security apps” that are actually malicious. If you encounter messages about viruses while browsing or see apps called “Guard Test” promising to scan and remove threats, these are likely scams attempting to trick you into installing unnecessary or harmful software.
Most iPhone malware issues happen when users jailbreak their devices or install apps from sources outside the App Store. Warning signs of potential malware include unusual battery drain, unexplained data usage, device overheating, or apps crashing frequently. Apple’s walled garden approach to security means that following best practices—like keeping iOS updated and only downloading apps from the official App Store—provides strong protection against most Trojan threats.
Step 1: Confirm the Infection
First, take a deep breath. While it’s rare for iPhones to be infected with trojan viruses due to Apple’s strict security protocols, it’s not impossible—especially if your device is jailbroken or you’ve downloaded apps from outside the App Store.
Here are a few red flags to watch for:
- Unexplained battery drain
- Overheating without heavy use
- Pop-ups appearing when Safari isn’t open
- Apps crashing unexpectedly
- Strange apps you don’t remember installing
- Unfamiliar charges on your Apple ID or mobile account
If you’re seeing several of these symptoms, there’s a good chance something’s wrong.
Step 2: Disconnect from the Internet
The moment you suspect a trojan, disconnect from Wi-Fi and cellular data:
- Swipe down to open Control Center.
- Tap Airplane Mode to stop all communications.
This prevents the trojan from sending or receiving data, reducing the risk of personal information being stolen.
Step 3: Delete Suspicious Apps Immediately
Look through your home screen and settings for any apps you didn’t install or that seem sketchy:
- Press and hold the app icon until the menu appears.
- Tap Remove App, then Delete App.
If you aren’t sure about an app, Google it. Be cautious with apps that aren’t from well-known developers or that ask for unnecessary permissions.
Step 4: Clear Safari History and Website Data
If the trojan came through a malicious website, clearing your browsing data can help:
- Go to Settings > Safari.
- Scroll down and tap Clear History and Website Data.
- Confirm by tapping Clear History and Data.
This removes cookies, cached files, and scripts that may be part of the infection.
Step 5: Update iOS to the Latest Version
Apple frequently patches security holes in iOS updates. Running outdated software makes you vulnerable:
- Open Settings > General > Software Update.
- If an update is available, tap Download and Install.
This often eliminates security issues exploited by trojans.
Step 6: Run a Security Check Using Apple’s Built-in Features
While iPhones don’t support traditional antivirus apps like Android devices do, you can still take advantage of Apple’s built-in tools:
- Check for unknown configuration profiles:
- Go to Settings > General > VPN & Device Management.
- Delete anything unfamiliar.
- Review app permissions:
- Open Settings > Privacy & Security.
- Scroll through each category (like Camera, Microphone, etc.) and look for apps with unnecessary access.
If something seems suspicious, revoke the permissions.
Step 7: Restore from a Clean Backup (Optional but Powerful)
If your iPhone is still acting strangely, consider wiping it and restoring from a backup made before the problem started:
- Back up your iPhone to iCloud or a computer if you haven’t already.
- Go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Erase All Content and Settings.
- Follow the prompts to reset your device.
- During setup, choose Restore from iCloud Backup or Restore from Mac/PC Backup, making sure the backup predates the infection.
If you don’t have a clean backup, set it up as a new device.
Step 8: Change All Your Passwords
Even if the trojan seems to be gone, your data could already be compromised. Act quickly:
- Change your Apple ID password.
- Update passwords for your email, banking apps, and any other critical accounts.
- Turn on two-factor authentication wherever possible for added security.
This helps prevent unauthorized access even if your credentials were stolen.
Step 9: Contact Apple Support
If you’ve done all the above and still think your iPhone has a trojan, reach out to Apple Support. They have diagnostic tools that can help confirm if your device is compromised. They can also guide you through more advanced troubleshooting.
Step 10: Learn How to Prevent Future Infections
Once your iPhone is clean, stay safe going forward:
- Don’t jailbreak your device—this bypasses Apple’s security controls and exposes you to malware.
- Download apps only from the App Store. Avoid sideloading apps from third-party sites.
- Keep iOS up to date.
- Be cautious with public Wi-Fi, and consider using a reputable VPN.
- Avoid clicking suspicious links, even if they appear to be from trusted contacts.
Key Takeaways
- Trojan viruses rarely affect iPhones but are more common on jailbroken devices that bypass Apple’s security protections.
- Warning signs of iPhone malware include unexpected pop-ups, battery drain, unusual data usage, and device performance issues.
- Protect your iPhone by keeping iOS updated, avoiding suspicious links, and only downloading apps from the official App Store.
Understanding Trojan Viruses
While trojans on iPhones are rare, they do happen. The key is to act quickly, stay calm, and follow these steps methodically. Keeping your device secure is an ongoing process, but it’s worth the peace of mind.
Trojan viruses pose a subtle yet significant threat to iPhone users. These malicious programs operate by disguising themselves as legitimate software while carrying out harmful activities behind the scenes.
Defining a Trojan Virus
A Trojan virus, also known as a Trojan horse, is a type of malware that masquerades as legitimate software while performing malicious actions without the user’s knowledge. The name derives from the Greek myth of the Trojan Horse, reflecting how these threats rely on deception to gain access to devices.
Unlike traditional viruses, Trojans don’t self-replicate. They require user interaction to install and execute. On iPhones, Trojans typically enter the system when users download apps from unofficial sources or click suspicious links.
Once installed, a Trojan can steal sensitive information, damage files, or create backdoor access for hackers. These malicious programs might monitor user activity, access personal data, or even add the iPhone to a botnet—a network of compromised devices controlled by attackers.
Differences Between Trojan Viruses and Other Malware
Trojans differ from other malware types in several key ways:
- Method of attack: Trojans rely on social engineering rather than technical vulnerabilities
- User interaction: They require users to install or execute them, unlike worms that spread automatically
- Appearance: Trojans appear useful or harmless while viruses often announce their presence through visible damage
Adware displays unwanted advertisements, while spyware secretly monitors users. Ransomware encrypts data and demands payment. Trojans, however, can perform multiple malicious functions while maintaining their disguise.
The greatest danger of Trojans is their versatility. They can act as delivery vehicles for other malware types, creating compound threats that are particularly difficult to detect and remove.
Prevalence of Trojans on iPhone
Trojan viruses on iPhones are relatively rare compared to Android devices, thanks to Apple’s strict App Store policies and iOS security features. However, the threat is real and growing.
Most iPhone Trojans target jailbroken devices since these bypass Apple’s security measures. Users who jailbreak their phones to access unauthorized apps face significantly higher risks of malware infection.
Common infection vectors include:
- Phishing websites and messages
- Fake apps that mimic legitimate software
- Compromised public Wi-Fi networks
Recent years have seen sophisticated iPhone Trojans like XcodeGhost and Pegasus emerge. These advanced threats demonstrate that even Apple’s secure ecosystem isn’t immune to malware. Security experts continue to identify new Trojan variants specifically designed to bypass iOS protections.
Despite their rarity, the potential damage from an iPhone Trojan infection can be severe, ranging from identity theft to financial loss and privacy violations.
Signs of Trojan Infection on iPhones
While iPhones are generally secure, they can still be infected with Trojan malware in rare cases. Detecting these infections early is crucial to protect your personal data and device performance.
Unexpected Pop-Ups
One of the most common signs of a Trojan virus on an iPhone is the sudden appearance of unexpected pop-ups. These intrusive advertisements might appear even when you’re not using a browser or when your phone is idle. Pop-ups promoting suspicious apps, fake prizes, or adult content are particularly concerning.
Pop-ups requesting unusual permissions or claiming your device is infected are classic malware tactics. These deceptive messages often use urgency or fear to trick users into downloading additional malicious apps or entering personal information.
Red flags to watch for:
- Pop-ups appearing on your home screen
- Messages claiming your iPhone needs cleaning or has viruses
- Redirects to unfamiliar websites when using Safari
- Prompts asking for Apple ID or password outside of normal settings
Sudden Decrease in iPhone Performance
A significant drop in your iPhone’s performance might indicate a Trojan infection running malicious processes in the background. Malware consumes system resources while stealing data or performing unauthorized activities.
Battery drain is particularly telling—if your iPhone suddenly loses power much faster than normal without explanation, it could be due to malware processes. Apps might also crash frequently or take longer to load than usual.
Performance indicators to monitor:
- Battery draining significantly faster than normal
- Device overheating without heavy usage
- Unexpected freezes or system crashes
- Apps taking unusually long to open or respond
- Overall sluggish performance compared to normal operation
Unusual Activity Within Apps
Trojans often manipulate legitimate apps or disguise themselves as trusted applications. Watch for unexpected behaviors within apps you regularly use, especially if they suddenly request new permissions or display unfamiliar interfaces.
Suspicious apps might send messages, make calls, or transfer data without your knowledge. Examining data usage can reveal malware activity—unexplained spikes in cellular or Wi-Fi data consumption often point to malicious background processes transmitting your information.
Signs to look for:
- Apps requesting unnecessary permissions
- New apps you don’t remember downloading
- Strange messages sent from your device
- Unusual charges on your phone bill
- High data usage from apps you rarely use
- Familiar apps behaving differently than normal
iPhone Security Measures
iPhones feature comprehensive security protections that help shield users from Trojan viruses and other malware. These safeguards work together to create multiple layers of defense that make iPhones significantly more resistant to threats than many other devices.
Apple’s Built-In Security Features
iOS utilizes a security architecture called “sandboxing” that isolates apps from each other and restricts their access to system resources. This prevents malicious apps from accessing data from other applications or taking control of core system functions.
The App Store review process adds another crucial layer of protection. Apple examines all apps before they’re published, checking for malware and ensuring they meet security standards. This significantly reduces the risk of downloading infected apps compared to third-party sources.
iOS also includes hardware-based security features. The Secure Enclave, a dedicated processor that handles sensitive data, keeps passwords, biometric information, and encryption keys separate from the main system. This protection means even if malware somehow accesses your device, it cannot easily steal your most sensitive information.
Face ID and Touch ID provide biometric authentication that’s both secure and convenient, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access to your device.
Importance of Regular Software Updates
Software updates are critical for maintaining iPhone security. Apple regularly releases patches that fix newly discovered vulnerabilities before they can be widely exploited by attackers.
These updates often address zero-day vulnerabilities – security flaws unknown to Apple until they’re discovered by researchers or, unfortunately, exploited by hackers. Prompt installation of these updates can prevent malware from taking advantage of these vulnerabilities.
iOS updates typically include enhancements to existing security features. Apple continuously improves protections like XProtect (which identifies and blocks known malware) and Gatekeeper (which verifies app authenticity).
To update your iPhone, go to Settings > General > Software Update. Enabling automatic updates is recommended for most users, as it ensures protection without requiring manual intervention.
Benefits of Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds a powerful extra layer of security to your Apple ID. With 2FA enabled, signing into a new device requires both your password and a verification code sent to your trusted devices.
This protection means that even if attackers somehow obtain your password, they still cannot access your account without physical access to your other devices. The verification codes are temporary and change with each login attempt.
2FA helps protect access to iCloud data, Apple Pay, App Store purchases, and other sensitive Apple services. It’s particularly effective against phishing attacks that attempt to trick users into revealing their passwords.
Setting up 2FA is straightforward. Go to Settings > [your name] > Password & Security > Two-Factor Authentication and follow the prompts. You can designate multiple trusted phone numbers to receive verification codes.
Lockdown Mode and Other Advanced Settings
Lockdown Mode provides exceptional protection for users who may be targeted by sophisticated attackers. When enabled, this feature strictly limits website functionality, blocks most message attachments, disables certain sharing features, and prevents incoming FaceTime calls from unknown contacts.
While most users won’t need this extreme level of protection, it’s valuable for journalists, activists, or business executives who face heightened security risks.
Privacy settings offer granular control over which apps can access features like your location, photos, microphone, and camera. Review these regularly at Settings > Privacy & Security.
App Tracking Transparency requires apps to request permission before tracking your activity across other companies’ apps and websites. This limits data collection that could potentially be exploited.
Content & Privacy Restrictions (found in Screen Time settings) can prevent unauthorized purchases and limit adult content, adding another layer of security particularly useful for family devices.
How Trojans Spread to iPhones
While iPhones are generally more secure than many other devices, they can still be vulnerable to Trojan infections through several vectors. These malicious programs disguise themselves as legitimate apps or files, tricking users into installing them and potentially compromising their personal data.
Through Phishing and Scam Text Messages
Cybercriminals frequently use phishing techniques to target iPhone users. They send deceptive text messages or emails that appear to come from trusted sources like Apple, banks, or popular services.
These messages typically contain urgent requests asking users to “verify” account details or fix security issues by clicking on a link. Once clicked, these links may lead to fake websites designed to steal login credentials or prompt the download of malicious profiles.
SMS phishing (smishing) has become increasingly sophisticated, with messages that mimic delivery notifications, account warnings, or prize announcements. These texts often create a false sense of urgency, pushing users to act without thinking.
Warning signs of phishing attempts:
- Unexpected messages about account problems
- Poor grammar or spelling errors
- Requests for personal information
- Suspicious links with unusual domains
- Messages creating undue urgency
Via Jailbreaking the Device
Jailbreaking removes Apple’s built-in security restrictions on iPhones, allowing users to install apps from outside the App Store. While this provides more customization options, it significantly compromises the device’s security framework.
Jailbroken iPhones bypass iOS’s app sandboxing feature, which normally prevents apps from accessing data from other apps. This creates an environment where malicious code can more easily infiltrate the system and access sensitive information.
Many Trojan infections occur when users download tweaks or modified apps from unofficial repositories after jailbreaking. These repositories lack Apple’s rigorous security screening process, making them prime distribution channels for malware.
The risks of jailbreaking include:
- Voiding your warranty
- System instability
- Increased vulnerability to malware
- No iOS security updates
- Potential data theft
Through Third-Party App Installations
Apple’s strict App Store review process helps prevent malicious apps from reaching users. However, enterprise certificates and developer profiles can be misused to distribute apps outside the App Store.
Some users attempt to install apps using configuration profiles or enterprise certificates that bypass Apple’s security measures. Cybercriminals exploit this by creating fake “free” versions of popular paid apps that contain hidden Trojans.
When users install these unauthorized apps, they often grant extensive permissions without realizing it. These permissions can give Trojans access to contacts, photos, location data, and even microphone or camera functionality.
The safest approach is to only download apps from the official App Store and to carefully review the permissions requested by each app. Suspicious permission requests for features unrelated to the app’s function should raise red flags.
From Visiting Fraudulent Websites
Malicious websites can trigger automatic downloads or display convincing pop-ups claiming the iPhone is infected with viruses. These sites often appear in search results or through redirects from compromised legitimate websites.
A common tactic involves displaying fake “virus warning” alerts that mimic iOS system messages. These alerts claim the device is infected and prompt users to install a “security app” that is actually malware. This exact scenario appears in the search results where users reported an app called “Guard Test” displaying such behavior.
Fraudulent websites may also exploit browser vulnerabilities or use social engineering tactics to trick users into installing device profiles. These profiles can modify system settings and potentially install malicious certificates.
Protection tips:
- Pay attention to fraudulent website warnings in Safari
- Never install profiles from unknown sources
- Be skeptical of any pop-up claiming your device is infected
- Keep iOS updated to protect against known browser exploits
- Use Safari’s built-in security features
Preventive Measures Against iPhone Trojans
Prevention is the best defense against iPhone Trojan infections. Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of malware compromising your device and personal data.
Downloading Apps From Trusted Sources
The App Store remains the safest source for iPhone applications. Apple’s rigorous vetting process helps prevent malicious software from reaching users. Users should avoid downloading apps from third-party sources or clicking on suspicious links that prompt installations.
Jailbreaking an iPhone may provide access to more customization options, but it removes crucial security protections. This practice bypasses Apple’s security features and exposes the device to potential Trojan infections.
Before downloading any app, users should check reviews and ratings. The number of downloads and review quality can indicate an app’s legitimacy.
It’s also important to verify the developer’s identity. Legitimate apps typically come from established companies with professional websites and support channels.
Utilizing Antivirus Apps and Scanners
While iPhones are generally secure, dedicated security apps provide an additional layer of protection. Reputable antivirus apps can detect suspicious activities and potential malware threats.
Users should choose security solutions from established cybersecurity companies. Many offer features beyond malware detection, including privacy protection and anti-theft tools.
Regular malware scans help identify potential threats before they cause damage. Most security apps allow users to schedule automated scans for continuous protection.
Some antivirus apps include web protection features that block malicious websites and phishing attempts. These tools can prevent Trojans from being downloaded in the first place.
Security apps with real-time monitoring can detect unusual behaviors that might indicate malware activity. This proactive approach stops threats before they compromise sensitive data.
Implementing Secure Network Practices with VPN
Public Wi-Fi networks pose significant security risks for iPhone users. Hackers can intercept data transmitted over these networks, potentially installing Trojans.
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts internet traffic, making it much harder for attackers to compromise the connection. This protection is especially important when using public Wi-Fi at cafes, hotels, or airports.
Users should choose a reputable VPN service with strong encryption standards. Free VPNs might compromise on security or even collect user data, defeating their purpose.
Many VPN apps offer additional security features like malicious site blocking. This adds another layer of protection against Trojan attacks through compromised websites.
Always verify network names before connecting. Attackers often create fake networks with names similar to legitimate ones to trick users into connecting.
Educating Yourself on Recognizing Scams
Many iPhone Trojans rely on social engineering rather than technical exploits. Learning to recognize common scams is crucial for protection.
Phishing attempts often arrive via email or text messages, claiming to be from Apple or other trusted companies. These messages typically create urgency and request personal information or prompt users to click suspicious links.
Pop-up warnings about viruses on iPhones are almost always scams. Apple doesn’t send such notifications, and legitimate security alerts don’t appear as browser pop-ups.
Users should be skeptical of “free” offers or unexpected prize notifications. These often lead to malicious sites that attempt to install Trojans.
Never share Apple ID credentials, passwords, or verification codes with anyone. Apple representatives will never ask for this information, and such requests are clear signs of scam attempts.
Responding to Trojan Infections
Dealing with a Trojan infection on an iPhone requires swift action to minimize damage and protect sensitive data. The following steps provide a systematic approach to removing malicious software and securing your device against future threats.
Steps to Remove Suspicious Apps
When facing a potential Trojan infection, identifying and removing suspicious apps is the first critical step. Users should carefully review all installed applications, focusing on any they don’t recognize or remember downloading.
To delete a suspicious app, press and hold its icon on the home screen until it jiggles. Tap the “X” that appears in the corner or the “Remove App” option in the menu. Confirm the deletion when prompted.
For a more thorough review, go to Settings > General > iPhone Storage, where apps are listed with their size and last usage date. This can help identify suspicious apps that consume excessive storage or haven’t been used despite showing recent activity.
Be particularly wary of apps that weren’t downloaded from the App Store. While rare on non-jailbroken iPhones, sideloaded apps pose significant security risks and should be removed immediately if discovered.
Clearing History and Website Data
Browser history and website data can harbor malicious code that enables Trojans to function. Clearing this data is essential for removing infection traces.
To clear Safari data, go to Settings > Safari > Clear History and Website Data. This removes browsing history, cookies, and other browsing data. For other browsers like Chrome or Firefox, open the app and find the clearing options in their respective settings menus.
Additionally, clear website data from Settings > Safari > Advanced > Website Data > Remove All Website Data. This eliminates stored data that might contain malicious scripts.
It’s also wise to check Settings > Safari > Block Pop-ups and ensure this feature is enabled. Pop-up blockers can prevent many common browser-based attack vectors used to deliver Trojans.
Changing Passwords and Managing Sensitive Data
After removing malicious apps, changing passwords is crucial to prevent unauthorized access. Start with Apple ID credentials by going to Settings > [your name] > Password & Security > Change Password.
For banking apps and other sensitive accounts, change passwords directly through those services’ official websites rather than through apps that might still be compromised. Use strong, unique passwords for each account.
Review which apps have access to sensitive information in Settings > Privacy. Check categories like Location Services, Contacts, Photos, and revoke permissions for any suspicious or unnecessary apps.
Consider enabling two-factor authentication for your Apple ID and other important accounts. This adds an extra security layer even if passwords are compromised.
Sensitive documents like identity cards or financial information should be removed from Notes, Files, or Photos apps until you’re confident the device is secure.
Complete iPhone Factory Reset
If Trojan symptoms persist after trying the above methods, a factory reset may be necessary. This erases all content and settings, effectively removing any malware.
Before resetting, back up important data to iCloud or a computer. However, avoid restoring from backups made after the infection occurred, as this could reintroduce the malware.
To perform a factory reset, go to Settings > General > Reset > Erase All Content and Settings. Enter your passcode and Apple ID password when prompted to confirm.
After the reset, set up the phone as a new device rather than restoring from a backup if possible. If a backup is necessary, consider using one created before the infection was detected.
Once reset, carefully reinstall only verified apps from the App Store and restore data selectively to avoid reintroducing any malicious elements.
Understanding Malware Scanning Tools
While iPhones are generally secure against malware, having the right tools to detect potential threats is essential. Scanning tools offer varying levels of protection for iOS devices, with some providing more comprehensive security features than others.
Popular Antivirus Apps and Their Features
Several trusted antivirus applications are available for iPhones, each with unique capabilities. Norton 360 provides comprehensive protection with features like Wi-Fi security scanning, web protection, and a password manager. The app offers real-time threat detection that guards against phishing attempts and malicious websites.
Malwarebytes focuses on simplicity and effectiveness, scanning for adware, potentially unwanted programs, and other threats. It’s particularly useful for identifying browser hijackers and removing suspicious configurations.
McAfee Mobile Security combines antivirus protection with anti-theft features, secure photo storage, and Wi-Fi scanning. Its media vault helps protect sensitive images and videos.
Other notable options include:
- Avast Security (free VPN, photo vault)
- Lookout (identity protection, theft alerts)
- Trend Micro Mobile Security (social media privacy scanning)
How Malwarebytes and Similar Tools Work
Antivirus tools for iOS work differently than their desktop counterparts due to Apple’s sandboxing restrictions. Instead of accessing system files directly, these apps focus on detecting suspicious behaviors, configurations, and connections.
Malwarebytes and similar tools scan for known malware signatures by checking browsing data, configuration profiles, and network connections. They identify potential threats by comparing findings against databases of known malicious code patterns.
For jailbroken iPhones, tools can perform deeper scans, as they have access to the file system. These scans can detect banking trojans like GoldPickaxe that target financial information.
Most scanning tools also check for phishing sites and suspicious links that cybercriminals use to trick users into revealing sensitive information. They analyze URL structures, certificate validity, and website reputation before allowing connections.
Limitations of Virus Scanners on iPhones
Apple’s strict security model significantly limits what third-party virus scanners can do on iOS. Unlike Android devices, iOS apps cannot scan other applications or system files directly due to sandboxing.
Most “virus scanners” on iPhones can only check for malicious profiles, suspicious web content, and network vulnerabilities. They cannot detect or remove malware that might bypass Apple’s security through vulnerabilities.
For non-jailbroken devices, scanners cannot:
- Access other apps’ data
- Scan system files
- Run continuously in the background
- Remove deeply embedded malware
This makes traditional antivirus less effective on iOS compared to other platforms. Scanners also struggle to detect sophisticated threats like zero-day exploits that don’t match known malware signatures.
When data theft occurs, it’s typically through phishing rather than traditional malware, making behavior monitoring more valuable than file scanning.
Alternatives to Traditional Antivirus Solutions
Since traditional virus scanners have limitations on iOS, users should consider alternative security approaches. Content blockers like 1Blocker or AdGuard can prevent malicious ads and tracking scripts from loading in Safari.
VPN services offer an additional layer of security by encrypting network traffic and masking your location. This helps protect against man-in-the-middle attacks when using public Wi-Fi networks.
Password managers like 1Password or Bitwarden generate and store strong, unique passwords, reducing the risk of credential theft. They also help users identify phishing attempts by recognizing when legitimate-looking sites have incorrect URLs.
Apple’s built-in security features provide robust protection:
- App Store vetting process
- System integrity protection
- Automatic security updates
- iCloud Keychain for password management
Regular backups to iCloud or computers using iTunes provide the ultimate safety net. If malware does infect an iPhone, restoring from a clean backup often resolves the issue without data loss.
Legal and Privacy Considerations
Trojan viruses on iPhones can have serious legal implications and privacy consequences. When malware infiltrates a device, it endangers personal information and may violate several regulations designed to protect consumers.
Implications of a Trojan Virus on Personal Information
When a Trojan virus infects an iPhone, it often targets sensitive personal information such as banking credentials, photos, messages, and login details. This unauthorized access creates significant privacy concerns.
Data theft resulting from Trojan infections may violate privacy laws like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. These regulations give users specific rights regarding their personal information.
Victims of data theft may have legal recourse against negligent app developers who created security vulnerabilities. Some malware can activate device cameras or microphones, potentially violating wiretapping laws.
Organizations that fail to protect customer data stored on compromised devices may face substantial fines. In 2023, several companies faced penalties exceeding $1 million for data breaches involving mobile devices.
Staying Compliant with Device Management Policies
Organizations must implement clear mobile device management policies to prevent Trojan infections on company-issued iPhones. These policies should outline approved app sources and security practices.
Regular security updates are both a technical necessity and often a legal requirement for businesses handling sensitive data. Companies should document their security measures to demonstrate compliance with industry regulations.
Many industries have specific compliance requirements for mobile devices. Healthcare organizations must adhere to HIPAA regulations, while financial institutions follow PCI-DSS standards.
Employee training on recognizing phishing attempts and suspicious links is essential for legal compliance. Organizations should implement remote wipe capabilities for lost or stolen devices to prevent data breaches.
Apple’s Enterprise Developer Program participants must follow strict guidelines or risk removal from the program and potential legal consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
iPhone users often encounter security concerns regarding trojan viruses. Here are answers to common questions about detection, removal, and prevention of these malicious threats on iOS devices.
What steps are involved in detecting a Trojan virus on an iPhone?
Detecting a trojan virus on an iPhone involves monitoring for unusual behavior. Users should watch for unexpected battery drain, overheating, strange pop-ups, or apps crashing frequently.
Performance issues like slowdowns or freezes can indicate malware. Unusual data usage patterns might show background activities from malicious software.
Look for unfamiliar apps that weren’t manually installed. Check for unauthorized charges on linked payment methods, as some trojans aim to steal financial information.
What is the procedure for removing a Trojan virus from an iPhone?
Start by updating iOS to the latest version, as Apple regularly patches security vulnerabilities. Delete any suspicious apps immediately, especially those not downloaded from the official App Store.
Clear website data and browsing history by going to Settings > Safari > Clear History and Website Data. This removes potentially harmful cookies or cache files.
If problems persist, perform a factory reset as a last resort. Back up important data first, then go to Settings > General > Reset > Erase All Content and Settings.
How can one check for viruses in the iPhone settings?
iOS doesn’t have a built-in virus scanner, but users can check for suspicious activities in settings. Review all installed apps under Settings > General > iPhone Storage to identify unfamiliar applications.
Check app permissions by going to Settings > Privacy to see which apps have access to sensitive features like camera, microphone, or location. Revoke permissions for suspicious apps.
Monitor battery usage patterns in Settings > Battery to identify apps consuming excessive power in the background, which might indicate malicious activity.
Can iPhones be compromised by Trojans through email?
Yes, iPhones can potentially be compromised through phishing emails. Attackers send deceptive messages with malicious links or attachments that can lead to trojan installations.
Users should never click on suspicious links or download attachments from unknown senders. Apple’s security measures typically prevent most email-based attacks, but vigilance remains important.
Some sophisticated phishing attempts might direct users to fake websites requesting Apple ID credentials, which can then be used to install malicious profiles or apps.
What are the indications of a Trojan virus infection on an iPhone?
Unexplained charges on phone bills or payment accounts often indicate malware. Excessive pop-up advertisements, especially when not using a browser, suggest adware infection.
The iPhone may run significantly hotter than normal or experience rapid battery depletion. Apps might crash frequently or operate differently than expected.
Some users report their device turning on or off by itself, or apps launching without being touched. Strange text messages sent from your device without your knowledge can also indicate compromise.
Does iOS issue official warnings about Trojan virus threats?
No, Apple does not issue pop-up warnings about virus threats on iOS devices. Any alert claiming to detect viruses on an iPhone is likely a scam designed to trick users into downloading malicious software.
Legitimate security notifications from Apple appear in Settings under a red badge icon, not as browser pop-ups. These messages don’t use alarming language about immediate threats or time-sensitive actions.
If you see a warning claiming your iPhone has viruses and promoting an app to remove them, it’s almost certainly fraudulent. Apple’s security model generally doesn’t require third-party antivirus solutions.