Browsing the web can feel like being followed. Websites track your moves to show you ads. But you can stop this. Safari’s “Prevent Cross-Site Tracking” feature blocks websites from following you across the internet.
This tool makes your web use more private. It stops sites from seeing what you do elsewhere. You’ll see fewer ads based on your browsing. Your data stays safer.
Cross-site tracking uses cookies to watch you online. Turning on this feature in Safari deletes these cookies. It keeps your web habits to yourself. You can browse with more peace of mind.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Blocks trackers | Fewer targeted ads |
| Deletes cookies | More privacy |
| Default setting | Easy to use |
Preventing Cross-Site Tracking in Safari
What is Cross-Site Tracking?
Cross-site tracking is a method used by websites and advertisers to track your online activity across different websites. They do this using tracking technologies like cookies, pixels, and scripts. This tracking allows them to build a profile of your interests and browsing habits. This profile can then be used for targeted advertising, personalized content, and other purposes.
How Safari Prevents Cross-Site Tracking
Safari has built-in features to prevent cross-site tracking. These features work to limit the ability of websites to track you across the web. Safari uses a combination of techniques to achieve this:
- Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP): This is Safari’s primary defense against cross-site tracking. ITP identifies and limits the use of tracking technologies, such as third-party cookies. It does this by classifying cookies based on how they are used. It then restricts access to those cookies that are used for tracking.
- Privacy Report: Safari offers a Privacy Report that shows you the trackers it has blocked. This report gives you insight into the tracking attempts on the websites you visit.
Turning On Prevent Cross-Site Tracking
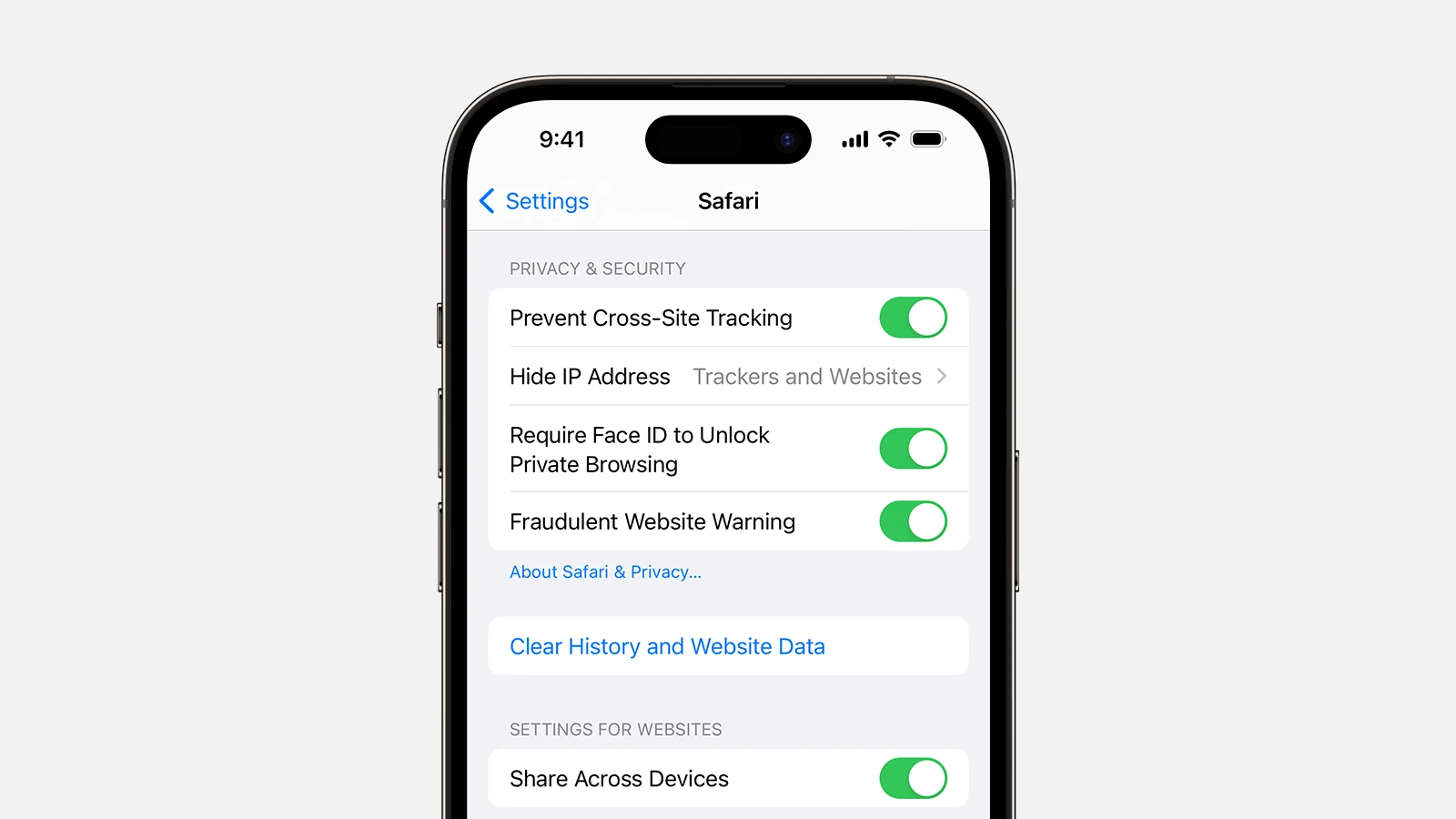
This feature is usually enabled by default. However, you can check and make sure it’s turned on by following these steps:
- Open the Settings App: Find and tap the “Settings” app on your iPhone or iPad’s home screen.
- Scroll Down and Tap “Safari”: Find “Safari” in the list of apps and tap it.
- Toggle “Prevent Cross-Site Tracking”: Make sure the switch next to “Prevent Cross-Site Tracking” is green (on).
Understanding First-Party vs. Third-Party Cookies
- First-Party Cookies: These cookies are set by the website you are directly visiting. They are often used for essential functions like remembering your login information or shopping cart items. Safari generally allows first-party cookies.
- Third-Party Cookies: These cookies are set by a domain different from the website you are visiting. They are often used for tracking purposes. Safari’s ITP focuses on limiting these cookies.
Viewing Safari’s Privacy Report
To see the trackers Safari has blocked:
- Open Safari: Launch the Safari browser on your device.
- Tap the “AA” Icon (or Share Icon on Older iOS): This is located in the address bar.
- Tap “Privacy Report”: This will show you a summary of the trackers Safari has prevented from profiling you.
Other Privacy Settings in Safari
In addition to preventing cross-site tracking, Safari offers other privacy settings:
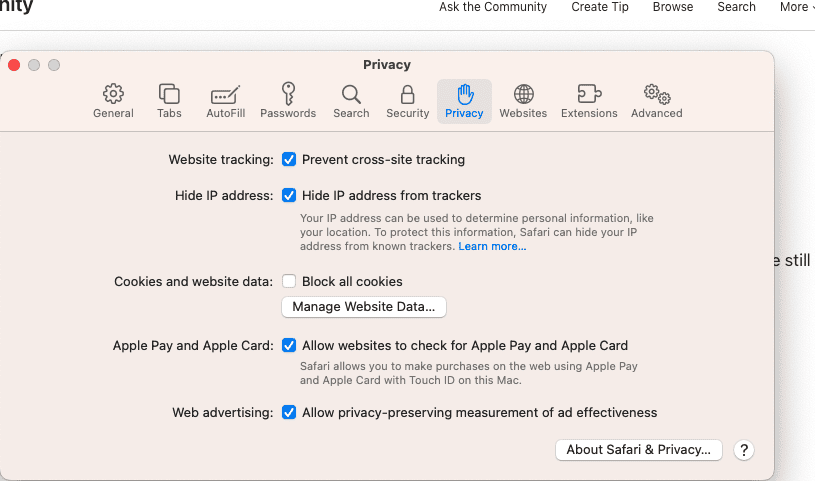
- Block All Cookies: This is a more aggressive setting that blocks all cookies, both first-party and third-party. This can break some website functionality.
- Hide IP Address: This feature hides your IP address from trackers, making it harder for them to identify you.
Why Protecting Your Privacy Matters
Protecting your online privacy is important for several reasons:
- Targeted Advertising: Cross-site tracking allows advertisers to create detailed profiles of you, which can lead to intrusive and unwanted ads.
- Data Breaches: Tracking data can be vulnerable to breaches, potentially exposing your personal information.
- Price Discrimination: In some cases, tracking can be used to show you different prices for the same products or services based on your browsing history.
Web browsers play a key role in online privacy. Features like Safari’s ITP help users control their online data. These tools are essential for navigating the modern web.
Understanding Cross-Site Tracking
The development of tracking prevention technologies is an ongoing process. As trackers become more sophisticated, browsers are improving their defenses. This continuous improvement helps protect user privacy online.
Cross-site tracking involves monitoring your online activities across different websites. It collects data about your browsing habits and preferences for various purposes.
The Basics of Tracking and Privacy
Cross-site tracking occurs when companies follow your online movements from one website to another. This practice lets advertisers and other entities build a profile of your interests and behaviors. They use this information to create targeted ads or personalize content.
Tracking often relies on cookies, small pieces of data stored in your browser. Third-party cookies are particularly useful for cross-site tracking. They allow trackers to recognize you across different websites.
Your privacy is at risk when extensive tracking occurs. Companies can gather sensitive information about your online activities without your knowledge. This data might include:
- Websites you visit
- Products you view
- Articles you read
- Videos you watch
How Trackers Collect Data
Trackers use various methods to gather information about your online behavior. Here’s a table outlining common tracking techniques:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Cookies | Small text files stored in your browser |
| Fingerprinting | Identifying your device based on its unique characteristics |
| Pixels | Tiny, invisible images embedded in web pages |
| Scripts | Code that runs in your browser to collect data |
Third-party trackers often embed their code on multiple websites. This allows them to follow you across the internet. They can piece together a comprehensive picture of your online behavior.
Advertisers use this data to create detailed user profiles. These profiles help them deliver highly targeted ads. While this can lead to more relevant content, it raises privacy concerns for many users.
Browser-Specific Protections
Different web browsers offer unique approaches to prevent cross-site tracking. These features aim to protect user privacy while browsing the internet.
Safari’s Approach to Privacy
Safari, Apple’s web browser, blocks potentially harmful trackers and limits cross-site tracking. It deletes cookies and website data from sites you haven’t visited in 30 days.
To enable this feature:
- Open Safari preferences
- Go to the Privacy tab
- Check “Prevent cross-site tracking”
Safari also offers Intelligent Tracking Prevention. This uses machine learning to identify and block trackers. It limits the lifespan of cookies set by third-party websites.
The Privacy Report feature shows you how many trackers Safari has blocked. You can access this by clicking the shield icon in the address bar.
Firefox’s Enhanced Tracking Protection
Firefox takes a strong stance on user privacy with its Enhanced Tracking Protection feature. It blocks social media trackers, cross-site tracking cookies, and cryptominers by default.
Firefox offers three levels of protection:
| Protection Level | What it blocks |
|---|---|
| Standard | Social media trackers, cross-site cookies, cryptominers |
| Strict | Everything in Standard plus fingerprinters and some scripts |
| Custom | You choose what to block |
To adjust these settings, go to Firefox Options > Privacy & Security. You can also view blocked trackers by clicking the shield icon in the address bar.
Firefox updates its list of known trackers regularly. This ensures you’re protected against the latest threats to your online privacy.
Technical Mechanisms to Prevent Cross-Site Tracking
Effective cross-site tracking prevention relies on multiple technical approaches. These methods work together to protect your privacy and limit unwanted data collection as you browse the web.
Cookie Management Strategies
Cross-site cookies are a primary tool for tracking users across websites. To combat this, browsers implement various cookie management techniques. Third-party cookies are often blocked by default, preventing trackers from storing data on your device. Some browsers use cookie partitioning, which isolates cookies to specific websites.
Another strategy is to automatically delete cookies after a set period. This limits the time trackers can use that data. You can also manually clear cookies or use private browsing modes to prevent persistent tracking.
Many browsers now implement intelligent tracking prevention. This system uses machine learning to identify and block tracking cookies while allowing necessary functionality.
IP Anonymization Techniques
Your IP address can be used to track your online activities. IP anonymization helps prevent this by masking or changing your visible IP address.
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) route your traffic through remote servers, hiding your real IP. This makes it harder for websites to pinpoint your location or link your activity across sites.
Tor (The Onion Router) offers even stronger anonymity. It routes your traffic through multiple encrypted nodes, making it extremely difficult to trace back to you.
Some browsers now offer built-in IP masking features. These route certain requests through proxy servers to hide your real IP from trackers.
Implementing Tracker Blockers
Tracker blockers are powerful tools for preventing cross-site tracking. These can be browser extensions or built-in features that block known tracking scripts and domains.
Popular blockers use regularly updated lists of tracking domains to prevent connections. Some use more advanced techniques like examining script behavior to identify and block new trackers dynamically.
Many blockers allow you to customize protection levels. You can choose to block all third-party content or allow certain trusted sites.
Some tracker blockers also include features to prevent browser fingerprinting. This technique uses your browser’s unique characteristics to identify you across sites.
| Blocker Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Built-in | Integrated, less resource-intensive | May be less customizable |
| Extension | Highly customizable, frequently updated | Can use more system resources |
| Network-level | Blocks trackers for all devices on network | Requires more technical setup |
Configuring Devices and Browsers for Enhanced Privacy
Protecting your online privacy requires careful configuration of your devices and browsers. You can take simple steps to limit tracking and enhance your digital security.
Adjusting iOS Privacy Settings
On your iPhone, you can easily manage privacy settings to reduce tracking. Go to Settings > Privacy > Tracking. Turn off “Allow Apps to Request to Track” to prevent apps from accessing your device identifier. This limits their ability to track you across apps and websites.
Next, visit Settings > Safari. Enable “Prevent Cross-Site Tracking” to block third-party content providers from tracking you. This feature helps protect your browsing habits from advertisers.
For social media apps, review their individual privacy settings. Limit data sharing and ad personalization options. Remember to regularly clear your browser cache and cookies to remove stored tracking data.
Managing Preferences on Desktop Browsers
Desktop browsers offer powerful privacy tools. In Safari, go to Preferences > Privacy. Check “Prevent cross-site tracking” to stop websites from tracking your behavior.
For Microsoft Edge users, click the three dots menu > Settings > Privacy and services. Choose your preferred tracking prevention level:
| Level | Description | Recommended for |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Blocks harmful trackers | Users who want minimal interference |
| Balanced | Blocks known harmful trackers and some third-party trackers | Most users |
| Strict | Blocks most trackers | Users prioritizing privacy |
Customize your tracking protection based on your needs. The “Strict” setting offers the most privacy but may break some websites.
Consider using privacy-focused browser extensions. These can block trackers, scripts, and ads that collect your data. Remember to update your browsers regularly to benefit from the latest privacy features.
Frequently Asked Questions
Cross-site tracking prevention is a crucial privacy feature in modern web browsers. It helps protect your online activity from being monitored across different websites. Let’s address some common questions about this important security measure.
What is the purpose of cross-site tracking prevention?
Cross-site tracking prevention aims to protect your privacy online. It stops advertisers and companies from following your browsing habits across multiple websites. This feature limits the data they can collect about you and your online activities.
How can I disable cross-site tracking on Safari?
To disable cross-site tracking on Safari:
- Open Safari settings
- Scroll down to “Privacy & Security”
- Toggle off “Prevent Cross-Site Tracking”
This will allow websites to track your activity across different sites.
Is it possible to prevent cross-site tracking on a MacBook?
Yes, you can prevent cross-site tracking on a MacBook. Safari on Mac includes this feature by default. To ensure it’s active:
- Open Safari
- Click “Safari” in the top menu
- Select “Preferences”
- Go to the “Privacy” tab
- Check the box next to “Prevent cross-site tracking”
What are the steps to enable cross-site tracking prevention on Chrome?
Chrome doesn’t have a specific “prevent cross-site tracking” option. But you can enhance your privacy:
- Open Chrome settings
- Go to “Privacy and security”
- Click “Cookies and other site data”
- Select “Block third-party cookies”
This setting helps limit cross-site tracking in Chrome.
Why is the option to prevent cross-site tracking grayed out in my settings?
If the option is grayed out, it might be due to:
- Using an older browser version
- Conflicting browser extensions
- Administrator settings on a work device
Try updating your browser or checking with your IT department if it’s a work computer.
What are the implications of turning off cross-site tracking prevention?
Turning off cross-site tracking prevention can:
- Allow advertisers to build a more detailed profile of your online activities
- Lead to more personalized ads across websites
- Potentially expose your browsing habits to third parties
It may also improve functionality on some websites that rely on cross-site data sharing.
| Browser | Default Cross-Site Tracking Prevention |
|---|---|
| Safari | On |
| Firefox | On |
| Chrome | Off (blocks third-party cookies) |
| Edge | Balanced (medium protection) |