The Apple Watch can’t tell you your blood pressure directly, but it can interface with other hardware (sold separately) that you can use to achieve this. On its own, Apple Watch can accurately offer you heart rate tracking and information about your sleep and health trends.
The Apple Watch does not have a built-in blood pressure monitor. Instead, users can connect their Apple Watch to third-party FDA-approved blood pressure devices to track and analyze their blood pressure readings over time. The accuracy of these readings depends on the external monitor used with the Apple Watch. The watch can track heart rate and blood oxygen levels, but it does not measure blood pressure directly. It serves as a tool to display and store data from a compatible blood pressure monitor, helping users manage their heart health and disease.
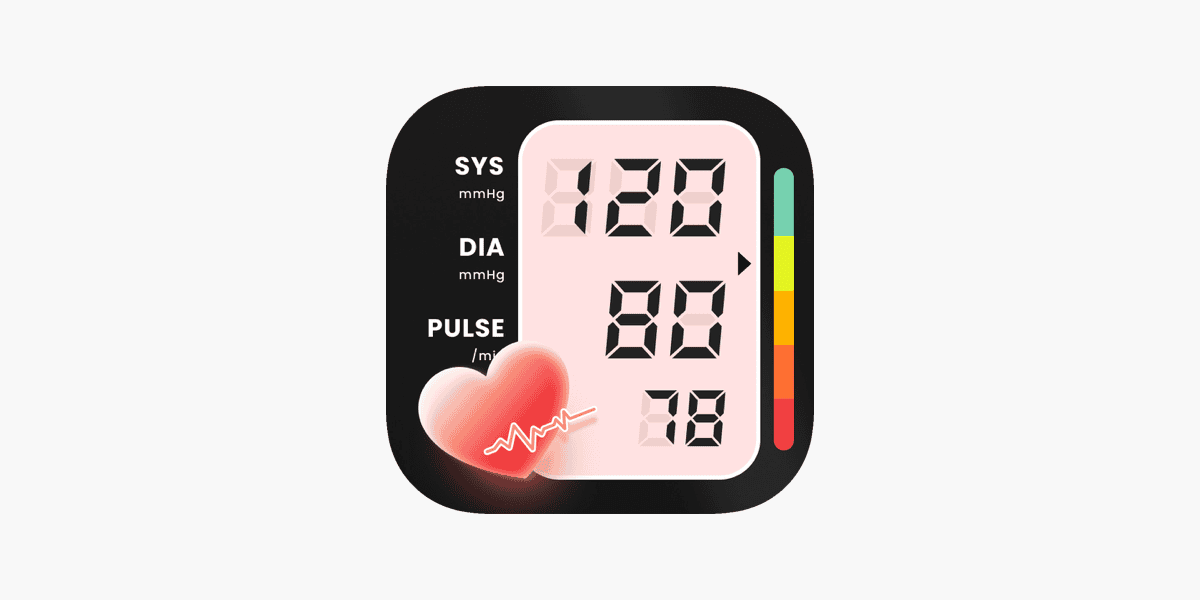
Taking Your Blood Pressure with Apple Watch: What You Need to Know
While the Apple Watch offers a wealth of health-tracking features, it does not directly measure blood pressure like a traditional cuff. Instead, it relies on third-party apps and devices that utilize the watch’s sensors and data to estimate blood pressure readings.
How Does It Work?
Several apps and devices claim to offer blood pressure monitoring capabilities for the Apple Watch. They typically employ one of two methods:
- Pulse Wave Analysis: This method analyzes the pulse wave patterns from your wrist using the watch’s heart rate sensor. Algorithms then estimate your blood pressure based on these patterns.
- Cuffless Blood Pressure Monitoring: Some external devices, like the QardioArm, use sensors and algorithms to measure blood pressure without the need for a traditional inflatable cuff. These devices connect to your Apple Watch to display and track readings.
Accuracy and Limitations
The accuracy of blood pressure readings from Apple Watch-compatible apps and devices can vary significantly. Here are some factors to consider:
- Validation and Clinical Studies: Look for apps or devices that have undergone rigorous testing and validation to ensure accuracy.
- Individual Factors: Several factors like body position, wrist size, and skin tone can affect the accuracy of readings.
- Calibration: Some devices require periodic calibration with a traditional blood pressure monitor to maintain accuracy.
Recommended Apps and Devices
| App/Device | Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| QardioArm | Cuffless | Requires separate device, FDA-cleared |
| WatchBP Home A | Pulse Wave Analysis | Subscription required |
| KardiaMobile 6L | ECG with pulse wave analysis | Requires separate device, FDA-cleared for irregular heart rhythm detection |
Important Considerations
- Consult Your Doctor: Always consult your doctor before relying on Apple Watch for blood pressure monitoring. It’s not intended to replace traditional medical devices.
- Use as a Reference: Treat Apple Watch blood pressure readings as a reference point, not a definitive diagnosis.
- Regularly Check Accuracy: If you’re using a cuffless device, calibrate it regularly with a traditional monitor.
Key Takeaways
- The Apple Watch can display blood pressure readings but requires an external device.
- Blood pressure data accuracy hinges on the third-party monitor’s precision.
- The watch assists with heart health management by tracking heart rate and blood oxygen levels.
Understanding Blood Pressure Monitoring on the Apple Watch
The Apple Watch offers a high-tech approach to health tracking, including the potential for blood pressure monitoring. To use this feature, third-party devices that interact with the watch are necessary.
The Technology Behind Blood Pressure Measurement
Apple Watch does not measure blood pressure directly. It requires an external blood pressure monitor, like QardioArm, which syncs data to the Apple Watch through Bluetooth. The Apple Watch uses sensors to monitor heart rate through a technique called photoplethysmography. This method detects blood flow through the wrist. But to get blood pressure readings, the watch must pair with a compatible device that can take the actual measurement.
Accuracy of the Apple Watch in Measuring Blood Pressure
When paired with an external monitor, the Apple Watch can display blood pressure readings. The accuracy of these readings depends not on the watch but on the external device. Users configure these devices with the Health app to feed accurate data to the watch. It’s vital to follow the setup instructions carefully to ensure accurate readings.
Comparison with Traditional Blood Pressure Monitors
Traditional blood pressure monitors typically use a cuff wrapped around the upper arm. This cuff inflates to measure the pressure inside the arteries. Readings from devices like the QardioArm are comparable to these traditional methods when used correctly. The Apple Watch facilitates easy access to this data, but it’s the paired accessory that determines the measurement’s precision.
The Role of the Apple Watch in Heart Health and Disease Management
The Apple Watch serves as a vital tool for monitoring heart rate and identifying irregular patterns that may signal heart conditions. It also aids in tracking physical activity, which is essential for maintaining heart health.
Monitoring Heart Rate and Detecting Irregularities
Apple Watch consistently checks the wearer’s heart rate, alerting them to abnormal rates that could indicate serious issues like atrial fibrillation. This condition may lead to stroke if left untreated. The watch’s ECG app allows users to perform an electrocardiogram and share the results directly with their doctor.
Exercise and Activity Tracking Contributions to Heart Health
Regular exercise is key to preventing heart disease. The Apple Watch tracks workouts, encouraging consistent activity with daily goals. It helps people stay motivated and informed about their fitness levels, which is important for a healthy heart.
Integrating Apple Watch Data with Medical Analysis
Data from an Apple Watch can be integrated into health apps on the iPhone, providing comprehensive insights for medical professionals. With permission, doctors can access this data to make informed decisions about diagnosis and management of heart conditions.







