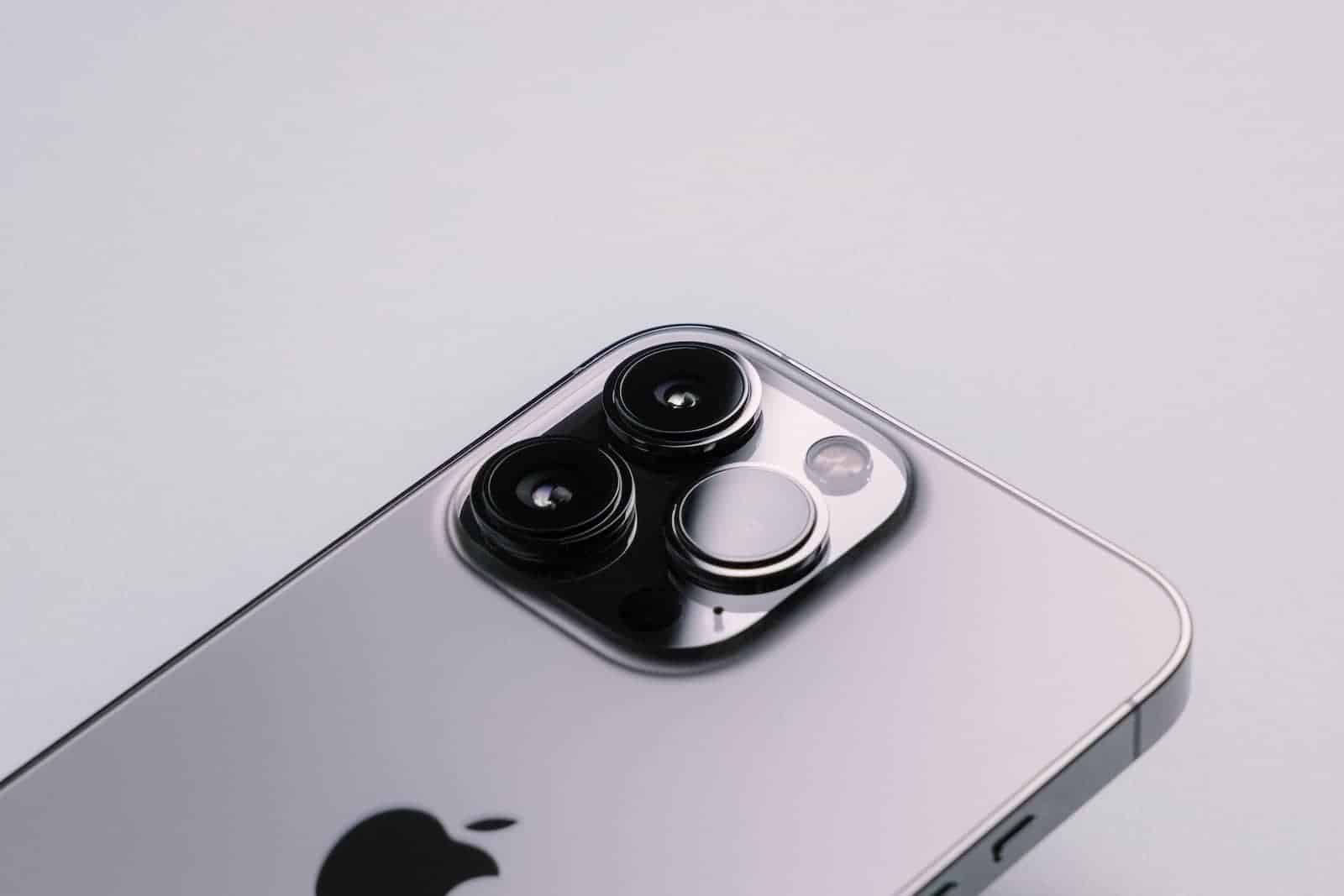
Using glass on the back of phones is a choice that balances how it looks, how well it works, and how long it lasts. Glass backs have pros and cons. They can look great, but they can also get damaged easily. So, why do most phone makers use glass backs even though they can break easily? Well, that’s because glass technology keeps getting better. Makers are always trying out new kinds of glass and treatments to make it tougher without making it heavier or thicker.
Glass backs are a big part of what’s coming next for smartphones. In the fast-changing world of smartphones, the material used for the back cover matters a lot for how it works and how it looks. Glass backs are common lately because of progress in technology, what people like in design, and how companies sell their products.
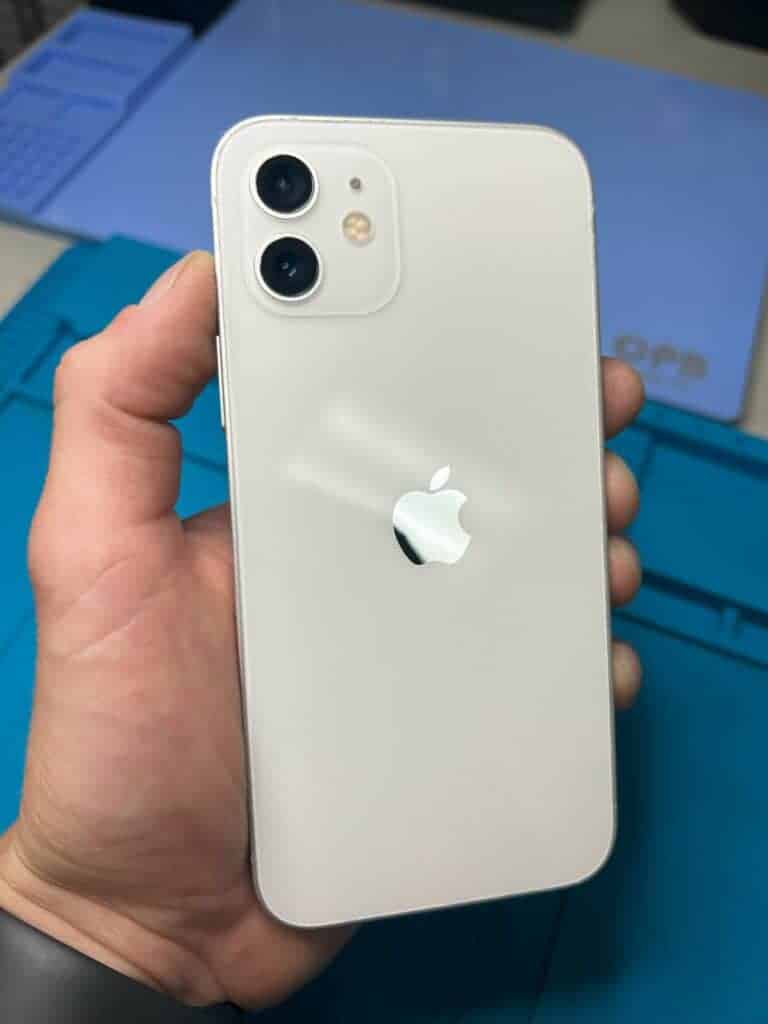

The Glass Back Phenomenon: Understanding the Shift in Smartphone Design
Wireless Charging Compatibility
One of the primary reasons for the prevalence of glass backs is their compatibility with wireless charging. Unlike metal, which can interfere with wireless charging signals, glass allows for efficient energy transfer, enabling convenient and cable-free charging.
Enhanced Aesthetics and Premium Feel
Glass backs contribute to a sleek, premium look and feel that resonates with consumers. They offer a smooth, glossy finish that exudes sophistication and can be customized with various colors and textures. Additionally, glass allows for unique design elements like transparent or translucent backs, showcasing internal components for a futuristic aesthetic.
Signal Transmission Optimization
Glass is more transparent to radio frequencies than metal, allowing for better signal transmission. This can result in improved cellular reception, Wi-Fi connectivity, and Bluetooth performance. While the difference might not be noticeable in all situations, it can be beneficial in areas with weaker signal strength.
Manufacturing and Design Flexibility
Glass is easier to mold and shape than metal, offering greater flexibility for manufacturers to experiment with different designs and form factors. This allows for curved edges, thinner profiles, and unique camera module integration. The malleability of glass also enables the creation of seamless, unibody designs that enhance the overall aesthetic appeal.
The Trade-Offs: Durability and Fragility
While glass backs offer numerous advantages, they come with a significant trade-off: fragility. Glass is more susceptible to cracking and shattering upon impact compared to metal or plastic. This necessitates the use of protective cases and screen protectors to safeguard the phone from accidental damage.
Alternatives to Glass Backs
Some manufacturers have explored alternatives to glass backs, such as ceramic or plastic, each with its own pros and cons. Ceramic offers a premium feel and scratch resistance but can be brittle. Plastic is more durable but may not exude the same level of sophistication.
The Future of Smartphone Design
As technology advances, we may see new materials and designs that offer the benefits of glass backs without the drawbacks. Innovations like stronger glass compositions, hybrid materials, or even self-healing backs could revolutionize smartphone design in the future.
Top Reasons For Back Glass
There are several reasons why cell phone manufacturers have increasingly adopted glass backs for their devices:
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Aesthetics and Premium Feel | Glass backs create a sleek, sophisticated, and high-end look that is often associated with luxury brands. The smooth, reflective surface can also be visually appealing and enhance the overall design of the phone. |
| Wireless Charging | Glass is one of the few materials that effectively allows electromagnetic waves to pass through, which is essential for wireless charging technology. Metal backs block these waves, making them incompatible with wireless charging. |
| Signal Reception | While not as significant as with metal backs, glass backs generally offer better signal reception compared to plastic backs. This is because plastic can sometimes interfere with radio waves, especially for higher frequency bands like 5G. |
| Heat Dissipation | Glass conducts heat better than plastic, which can help to improve the phone’s thermal performance and prevent overheating. This is particularly important for phones with powerful processors and large batteries that generate more heat. |
| Durability | Modern glass used in phone backs is often strengthened with technologies like Corning Gorilla Glass, making it more scratch-resistant and less prone to shattering than regular glass. However, glass backs are still generally more fragile than metal or plastic backs and require extra care to avoid damage. |
The Allure of Glass
A Touch of Luxury
Have you ever wondered why your smartphone feels so sleek and premium? One of the key reasons is the glass back. It’s not just about aesthetics; glass offers a level of sophistication and style that other materials can’t match. When you hold a phone with a glass back, you’re holding a piece of modern design that speaks to both luxury and technological advancement.
Wireless Charging
But it’s not all about looks. One of the most functional benefits of having a glass back is wireless charging. Glass allows for efficient energy transfer, making it easier to charge your phone without the hassle of cords. This feature has become increasingly important as wireless charging becomes more prevalent in public spaces and homes.
Signal Reception
Another less-known advantage of glass backs is improved signal reception. Unlike metal, which can interfere with signal strength, glass allows for better connectivity. This means fewer dropped calls and faster data speeds, keeping you connected in more places.
Durability
Now, let’s talk durability. While glass might seem fragile, manufacturers have been working hard to strengthen it. Technologies like Gorilla Glass have made phone backs more resistant to scratches and breaks. However, it’s a delicate balance – the more durable the glass, the thicker and heavier it becomes.
Scratch Resistance
Glass backs also offer superior scratch resistance compared to metal or plastic. This means your phone stays looking new for longer, maintaining its resale value and aesthetic appeal. A minor scratch on a metal back can be quite noticeable, but glass handles everyday wear and tear with more grace.
The Environmental Perspective: Glass vs. Plastic
From an environmental standpoint, glass is a more sustainable choice than plastic. It’s recyclable and doesn’t degrade over time, making it a friendlier option for our planet. As we become more conscious of our environmental impact, this factor becomes increasingly important.

The Downside: Fragility and Cost
However, it’s not all positive. The major downside of glass backs is their fragility. A drop without a protective case can lead to cracks or shatters, leading to costly repairs. This fragility has led to a rise in the use of protective cases, somewhat negating the aesthetic appeal of the glass back.
FAQs
Can wireless charging work with materials other than glass?
Yes, wireless charging can work with materials other than glass, although glass is often preferred due to its low interference with wireless charging signals. Some other materials that can be used for wireless charging include certain types of plastic and ceramic. However, these materials may require additional components or design considerations to ensure efficient charging.
Are glass backs more environmentally friendly than plastic?
Glass backs are generally considered less environmentally friendly than plastic backs. Glass production requires high temperatures and energy consumption, leading to a larger carbon footprint. Additionally, glass is more difficult to recycle than plastic, further impacting its environmental impact.
Is it necessary to use a case with a glass-backed phone?
While not mandatory, using a case with a glass-backed phone is highly recommended. Glass is more prone to shattering or cracking upon impact compared to plastic. A case provides a protective layer, significantly reducing the risk of damage from drops or accidental bumps.
How does the weight of a glass back compare to other materials?
Glass backs tend to be heavier than plastic backs, adding some extra weight to the overall phone. However, the difference in weight is usually not significant enough to be a major concern for most users.
Are glass backs more expensive to manufacture?
Yes, glass backs are generally more expensive to manufacture than plastic backs. The production process for glass involves higher temperatures and more complex techniques, increasing the manufacturing cost.
Do glass backs affect the resale value of a phone?
Glass backs can positively impact the resale value of a phone, particularly for high-end models. The premium look and feel of glass contribute to a more luxurious aesthetic, which can be appealing to potential buyers. However, any scratches or cracks on the glass back can significantly lower the resale value.
How do glass backs impact the overall design of a phone?
Glass backs offer a sleek and modern aesthetic, enhancing the overall design of a phone. They also allow for wireless charging capabilities and improved signal transmission for certain features like NFC. However, glass backs can be more prone to fingerprints and smudges, requiring frequent cleaning.
Are there any alternatives to glass that offer similar benefits?
Yes, there are a few alternatives to glass that offer similar benefits. Ceramic is a durable and scratch-resistant material that can also support wireless charging. However, it is generally more expensive than glass. Some manufacturers have also explored using composite materials that combine the strength of metal with the wireless charging capabilities of glass, providing a balance between durability and functionality.